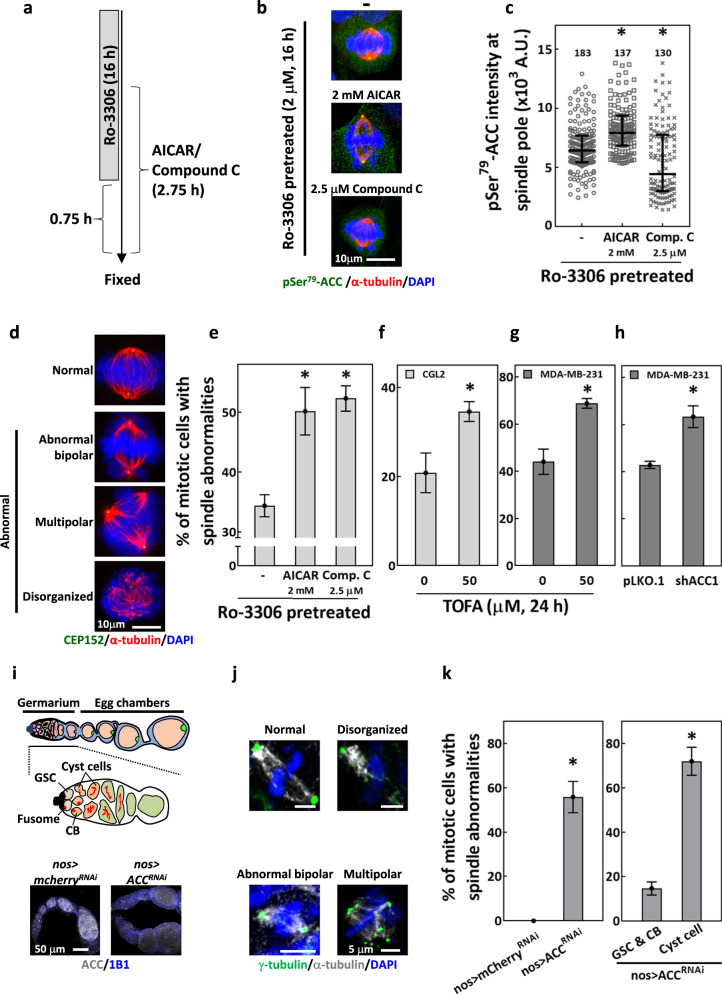
Fig. 2. Disrupting ACC activity induces defects in mitotic spindles.
a–e Disruption of ACC-Ser79 phosphorylation-induced spindle defects. a Protocol for Ro-3306 block and release and treatments of AICAR and compound C. The cell cycle of CGL2 cells was arrested and synchronized before mitosis entry by 16-h Ro-3306 treatment. For the last 2 h of Ro-3306 incubation, AICAR or compound C was added into the culture medium. After the 16-h incubation, Ro-3306 was washed away and cells were kept in medium containing AICAR or compound C for another 45 min. b Representative images of the Ro-3306-block-and-release-enriched mitotic cells; cells were untreated (−) or treated as indicated and stained for pSer79-ACC (green), α-tubulin (red), and with DAPI (blue). c AICAR increased pSer79-ACC, while compound C decreased the level of pSer79-ACC at the SP. The relative intensity of pSer79-ACC at the SP of the mitotic cells (as in b) was measured and presented in the scatter plot with the interquartile distribution from two independent experiments. The numbers above indicate the number of the SP measured. *P < 0.05 compared to untreated by Mann–Whitney Rank Sum test. d Representative images of mitotic cells with normal spindle or abnormal spindles stained for CEP152 (green), α-tubulin (red) and DAPI (blue). e Percentages of abnormal spindle-containing mitotic cells collected after the protocol described in (a) are shown as mean ± SD of at least 600 cells from two independent experiments. *P < 0.05 compared to untreated by Student’s t test. f, g ACC inhibition by TOFA-induced mitotic spindle abnormalities. Percentages of abnormal spindle-containing mitotic cells, untreated or treated with TOFA as indicated, are shown as mean ± SD of at least 400 cells from two independent experiments for CGL2 (f) and MDA-MB-231 (g). *P < 0.05 compared to untreated by Student’s t test. h Percentage of control (pLKO.1) and ACC1-depleted (shACC1) mitotic MDA-MB-231 cells with abnormal spindle are shown as mean ± SD of at least 400 cells from two independent experiments. *P < 0.05 compared to pLKO.1 by Student’s t test. i–k Knockdown of ACC-induced spindle abnormalities in Drosophila germaria. i, top: The schematic illustration of Drosophila germarium and egg chambers (upper scheme) and the magnified view of the germarium (lower scheme). Drosophila germarium each house 2–3 germline stem cells (GSCs) that asymmetrically divide to generate cystoblasts (CBs); each CB then undergoes four rounds of incomplete division to generate a 16-cell cyst. i, bottom: One-week-old control (nos > mCherryRNAi) and ACC knockdown (nos > ACCRNAi) ovarioles were stained for ACC (gray) and co-stained for 1B1 (blue, somatic cell membranes) to examine knockdown efficiency. j Representative images of the indicated types of mitotic spindles in Drosophila germ cells stained for γ-tubulin (green), α-tubulin (gray), and DAPI (blue). k, left: Percentage of mitotic cells in nos > mCherryRNAi and nos > ACCRNAi germ cells within germaria with abnormal spindles (including abnormal bipolar spindle, disorganized spindle, and multipolar spindle; as shown in j). Mean ± SD of at least 100 cells from two independent experiments is shown. k, right: The mitotic germ cells in nos > ACCRNAi germaria were identified as GSCs, CBs, and Cyst cells, and the percentages of mitotic cells with abnormal spindles from each cell type are shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared to pLKO.1 by Student’s t test.