Figure 1.
Identification of candidate SARS-CoV-2 CD8 T cell epitopes from eluted HLA class I ligands and by prediction
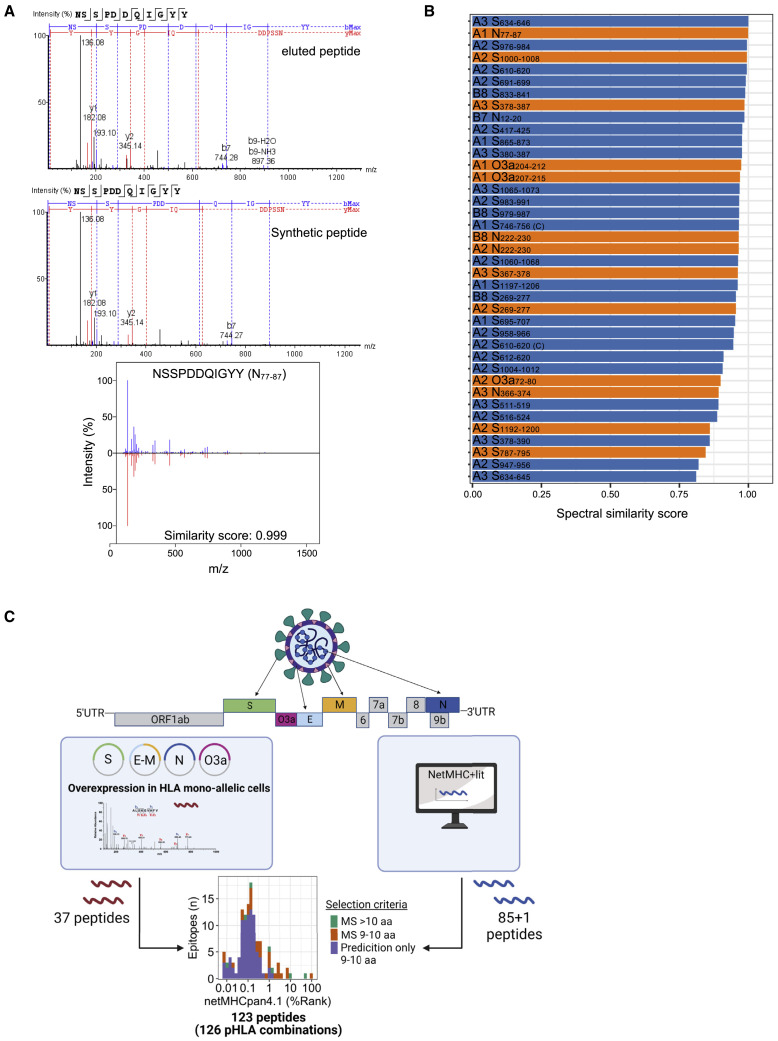
(A) Representative MS/MS fragmentation spectra of eluted and synthetic HLA class I peptide (N77–87) identified from mono-allelic B721.221 cells expressing the SARS-CoV-2 protein and calculation of similarity score using the SpectrumSimilarity function in the R package OrgMassSpecR.
(B) Display of peptides identified by MS in the exploratory approach considered as true identifications based on the calculation of the similarity score between the exploratory and synthetic peptide (score ≥0.8; n = 37). Orange bars represent peptides that were found to be true epitopes in subsequent analysis of T cell responses (data shown in Figures 2, 3 and Table 1). Labels show HLA restriction (A1 = HLA-A∗01:01; A2 = HLA-A∗02:01; A3 = HLA-A∗03:01; B7 = HLA-B∗07:02; B8 = HLA-B∗08:01) and peptide name.
(C) Schematic outline of peptide selection. Thirty-seven HLA class I-restricted peptides from SARS-CoV-2 proteins expressed in mono-allelic B721.221 cells were identified by MS, an additional 85 by prediction (NetMHCpan4.1 [BA-Rank < 0.2%]; NetMHC4.0 [Rank < 0.25%]), and one from literature, yielding a total of 123 peptides (126 pHLA combinations) (Table S1). UTR, untranslated region.