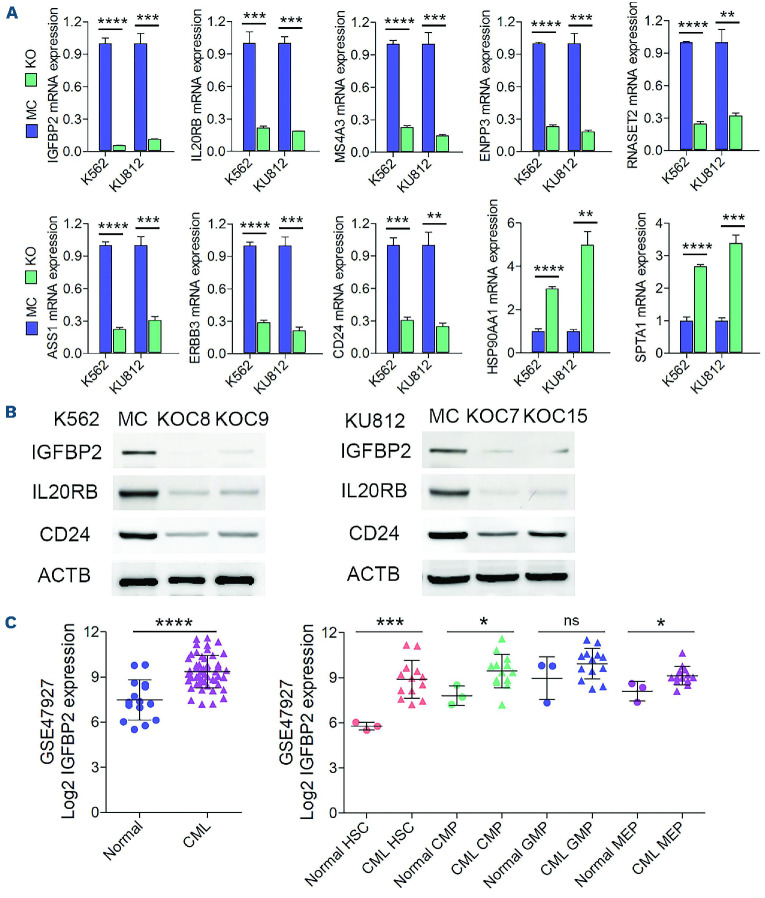
Figure 4.
Detection of the expression levels of potential RHOA downstream targets in chronic myeloid leukemia cells and primary patients’ samples. (A) Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis was used to verify differential expression of several of the most highly downregulated and upregulated genes in K562 RHOA knockout (KO) cells compared with mock control (MC) cells (N=3). Analysis of the same genes in the KU812 RHOA KO cells using RT-qPCR showed the same differential expression patterns. (B) The reduced expression levels for IGFBP2, IL20RB and CD24 were further confirmed using western blotting. (C) Analysis of the GSE47927 chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) dataset revealed a highly significant difference in IGFBP2 expression in CML samples (n=52) compared with normal controls (n=15). When cells from these CML cases were sub-fractionated into different stem/progenitor subpopulations, there was a highly significant increase in IGFBP2 expression in CML hematopoietic stem cells compared with normal counterparts. In similar comparisons, a significant increase in IGFBP2 expression was seen in common myeloid progenitors and megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitors but no difference was seen in granulocyte-monocytic progenitors. Statistical significance was established using the Student t test. **P≤0.001, ***P≤0.0001, ****P≤0.00001. HSC: hematopoietic stem cells; CMP: common myeloid progenitors; GMP: granulocyte-monocytic progenitors; MEP: megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitors.