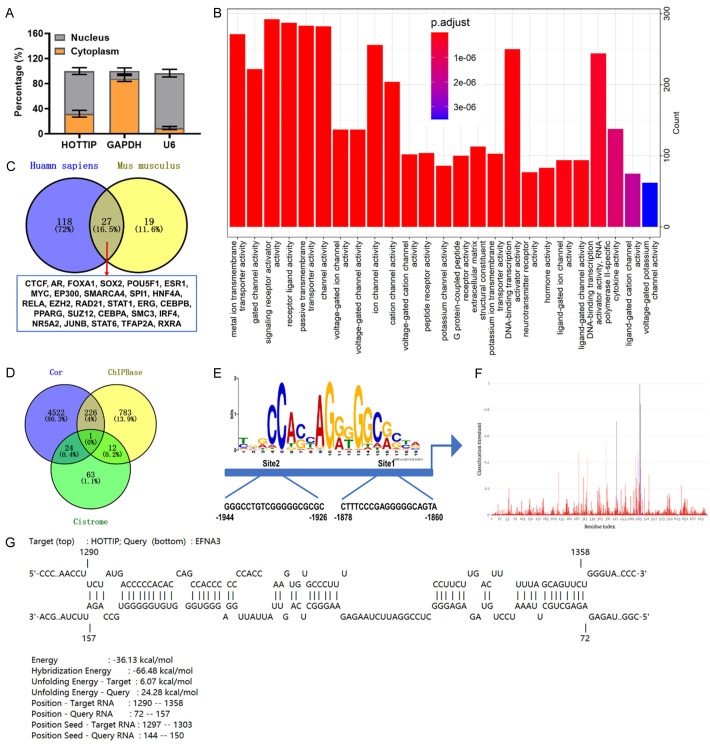
Figure 5.
Relationship among HOTTIP, CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) and Ephrin A3 (EFNA3) promoter. A: The percentage of HOTTIP in the cytoplasm and nuclear fractions was determined by nuclear fractionation analyses and qRT-PCR. B: Gene ontology (GO) analysis was performed for HOTTIP-related genes, and the molecular function categories were represented. C: The binding proteins of HOTTIP in Homo sapiens (Blue) and Mus musculus (yellow) were identified by RNAInter database. D: Venn diagram was used to confirm the common targets between HOTTIP-related genes and CTCF targets predicted by ChIPBase database and Cistrome database. E: The JASPAR database was used to predict the CTCF binding motif. F: The binding of HOTTIP to CTCF was predicted by PRIdictor databse. G: The binding site and interaction energy between HOTTIP and EFNA3 promoter were predicted by IntaRNA databse.