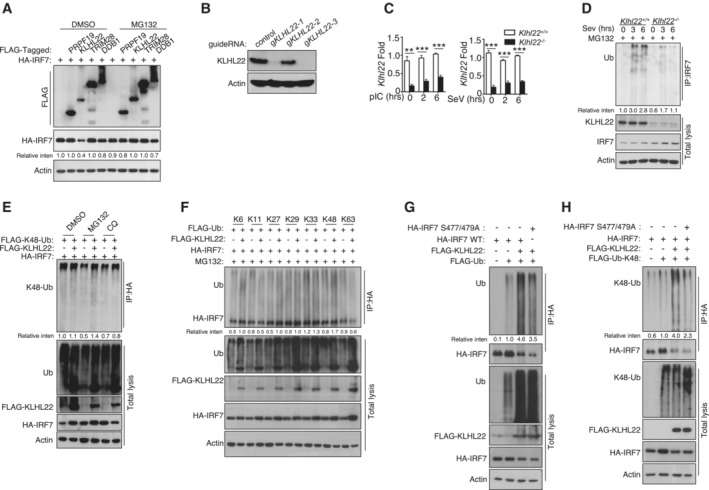
Figure EV4. KLHL22 mediates K48‐linked ubiquitination of IRF7 and promotes its degradation.
-
AHEK293T cells were transfected with IRF7 and the indicated expression plasmids. After treatment with MG132, the indicated proteins were detected by IB.
-
B, CIB and qRT–PCR analysis showing specific ablation of KLHL22 in KLHL22‐KO MEFs generated by CRISPR.
-
DAfter treatment with MG132, IRF7 was isolated by IP from whole‐cell lysates (WLs) of KLHL22‐KO MEFs and subjected to IB using anti‐ubiquitin. Total cell lysates were also subjected to direct IB.
-
EHEK293T cells were transfected with IRF7 and FLAG‐K48‐ubiquitin in the presence (+) or absence (−) of KLHL22 expression plasmids. After pretreatment with MG132 or CQ, HA‐tagged IRF7 was isolated by IP, and the ubiquitination level was then measured by IB.
-
FHEK293T cells were transfected with multiple ubiquitin mutants (mutations at K6, K11, K27, K29, K33, K48, and K63) and the indicated expression plasmids. HA‐tagged IRF7 was isolated by IP, and the ubiquitination level was then measured by IB.
-
G, HHEK293T cells were transfected with HA‐tagged IRF7 and the inactive mutant variants (S477 and 479A) whose phosphorylation sites at serine 477 and 479 were mutated from serine to alanine. HA‐tagged IRF7 was isolated by IP, and the ubiquitination level was then measured by IB.
Data information: Data from the qPCR assay are presented as the fold change relative to the Actin mRNA level. Data are represented as the means ± SDs. The data are representative of at least three biologically independent experiments.
Please see Appendix Fig S7 for information regarding replicates, quantification, and statistical evaluation for biochemical data in this figure.
Source data are available online for this figure.
