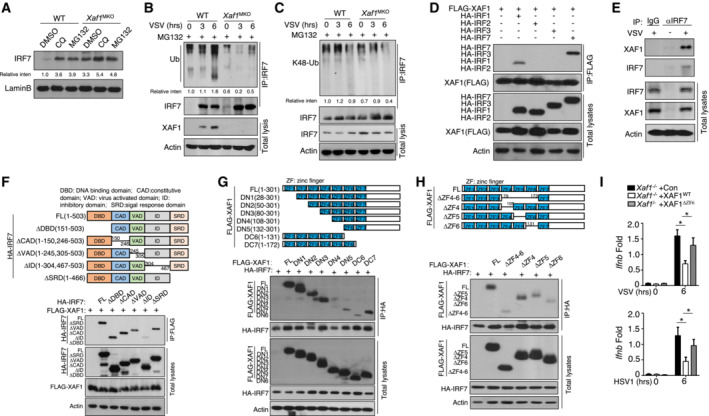
Figure 5. XAF1 promotes the ubiquitination of IRF7.
-
AAfter treatment with CQ or MG132, IRF7 in nuclear extracts of WT and XAF1‐deficient BMDMs was detected by IB.
-
B, CWT and XAF1‐deficient BMDMs were infected with VSV‐WT (MOI = 1) and treated with MG132 for 2 h before harvest. Whole‐cell lysates (WLs) were subjected to IP using an anti‐IRF7 antibody, and the indicated proteins were detected by IB.
-
DHEK293T cells were cotransfected with XAF1 and distinct IRF‐expressing plasmids. IB HA was performed followed by IP with an anti‐FLAG antibody.
-
EThe interaction between XAF1 and IRF7 was assessed in WT BMDMs stimulated by VSV‐WT (MOI = 1). WLs were subjected to IP using an anti‐IRF7 or anti‐IgG antibody and then to IB and detected with anti‐XAF1 antibody.
-
FThe associations between XAF1 and various IRF7 truncation mutants were detected through IP and IB of the transfected HEK293T cells.
-
G, HThe associations between IRF7 and various XAF1 truncation mutants were detected through IP and IB.
-
IqRT–PCR analysis of the indicated genes in XAF1‐deficient MEFs expressing XAF1WT and XAF1ΔZF6 and subjected to the indicated virus stimulation.
Data information: Data from the qPCR assay are presented as the fold change relative to the Actin mRNA level. The data are presented as the means ± SDs and are representative of at least three biologically independent experiments. The statistical analyses revealed variations among the experimental replicates. Two‐tailed unpaired t‐tests were performed. *P < 0.05.
Please see Appendix Fig S3 for information regarding replicates, quantification, and statistical evaluation for biochemical data in this figure.
Source data are available online for this figure.
