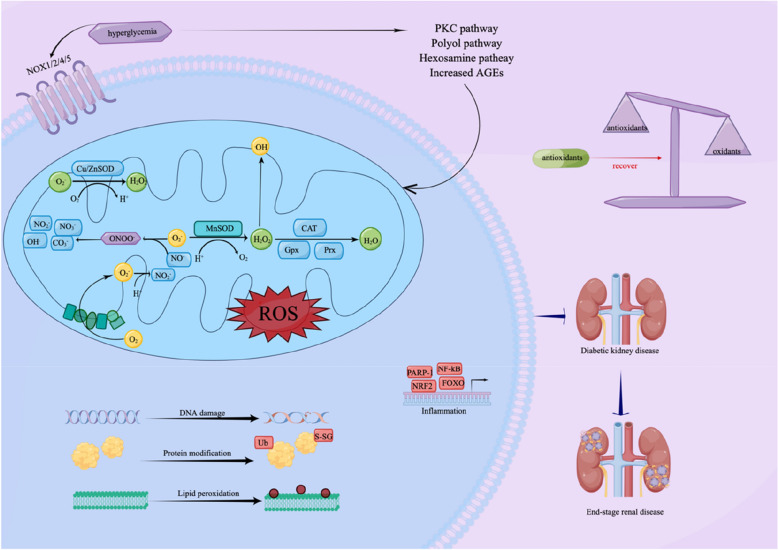
Fig. 1.
Oxidative stress is involved in the pathogenesis of DKD. Copper/zinc superoxide dismutase (Cu/ZnSOD) and manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) catalyze the mutation (or distribution) of superoxide (O2• −) radicals to hydrogen peroxide (H202) in the mitochondrial membrane space (IMS) and matrix, respectively. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is converted to water by catalase (CAT) and a group of glutathione peroxidases (gpx) and peroxide reductases (Prxs). H2O2 spreads easily to other parts of the mitochondria or cytoplasm. O2—reacts with nitric oxide (NO•) to produce peroxynitrite (ONOO-), ONOO- decomposes into highly oxidized intermediates such as NO2 − , OH•, CO3 − , etc., and finally forms stable NO3 − . NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; Nrf2, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2; PARP-1, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases; FOXO, forkhead box protein O. ROS, reactive oxygen species