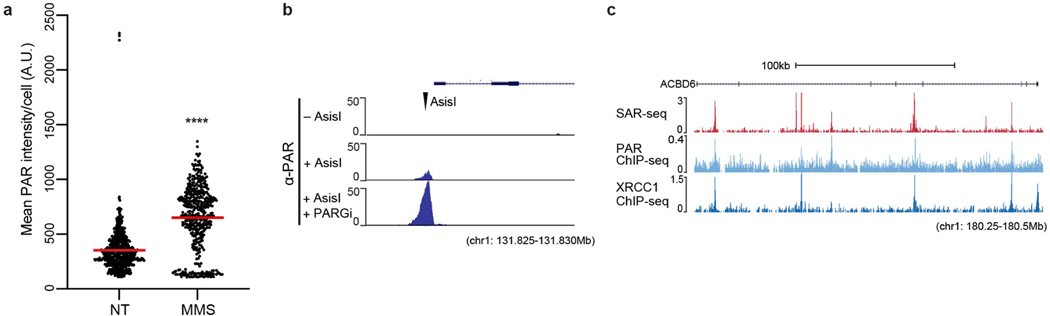
Extended Data Fig. 7 |. PARP and XRCC1 recruited to DNA repair sites.
a, Quantification of PAR levels with (n = 422 cells) and without (n = 541 cells) MMS treatment (red line, mean). Each dot represents one cell. Statistical significance was determined using two sided Mann–Whitney test (****P < 0.0001). Data are representative of three independent experiments. b, Anti-ADP-ribose ChIP–seq signal (n = 1) at an AsiSI restriction enzyme cut site (tick mark) in Abelson virus-transformed mouse pre-B cells. Cells were arrested in G0, and AsiSI double-strand breaks were induced for 18 h before ChIP. ADP-ribose is enriched at cleaved AsiSI sites and is increased by 20 min treatment with PARGi before fixation (AsiSI + PARGi), which is indicative of the presence of PAR. c, Genome browser screenshot illustrating the overlap between SAR-seq (n = 3), PAR (n = 1) and XRCC1 (n = 1) ChIP–seq signals in i3Neurons. Cells for PAR ChIP–seq were incubated with PARGi for 20 min before fixation.