Figure 4.
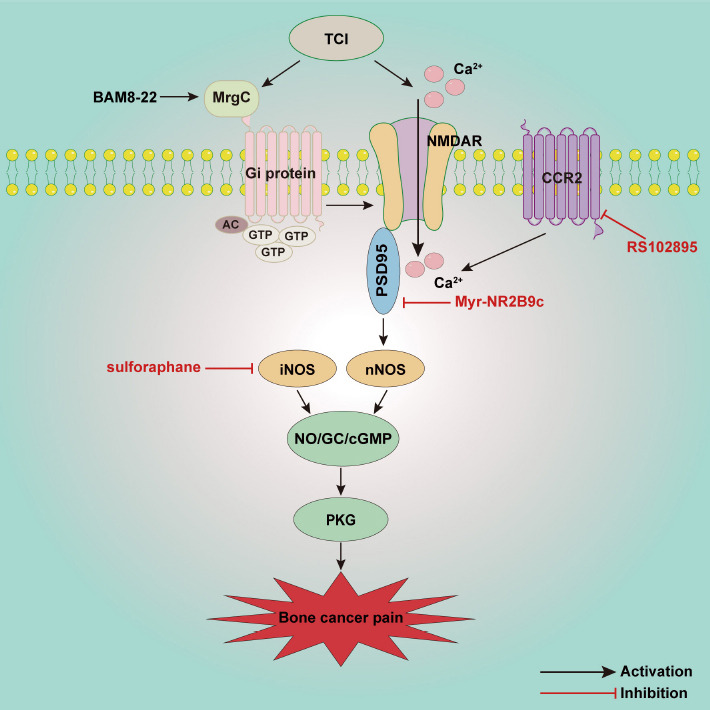
Schematic illustration of potential mechanisms involved in the NO/cGMP signaling pathway in bone cancer pain.
Activated NMDAR receptor promotes the activation of PSD95 and nNOS, and then induces activation of the NO/cGMP/PKG-I signal pathway, which is involved in the development of bone cancer pain. MrgC induces the activation of Gi protein, which in turn reduces spinal NMDAR-NR2B and nNOS and alleviates pain behavior. CCR2 also improves the activation of NMDAR and nNOS in the spinal cord. AC: Adenylate cyclase; CCR2: chemokine C-C motif receptor 2; cGMP: cyclic guanosine 3′,5′-monophosphate; GC: guanylate cyclase; Gi protein: inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins; MrgC: Mas oncogene-related gene C receptors; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors; nNOS: neuronal NOS; NO: nitric oxide; PKG: protein kinase G; PSD95: postsynaptic density protein 95; TCI: tumor cell implantation.
