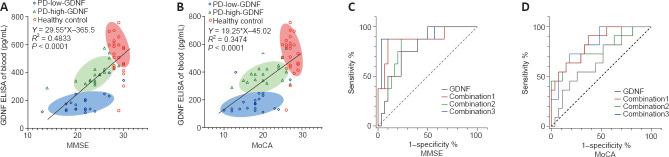
Figure 2.
Linear correlation analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for predicting the degree of cognitive impairment.
(A, B) A positive linear correlation (Spearman correlation) was observed between the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) (A) and between the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) score and GDNF (B). The oblique line represents the linear relationship. The linear regression equations are listed respectively. Ellipses of different colors represent different subgroups. The long axis of the ellipse represents the linear relationship of each subgroup. (C, D) The single serum GDNF indicator and the composite index predicted the ROC curve for varying degrees of cognitive impairment based on cognitive evaluations using the MMSE (C) and MoCA (D). Combination 1: education, Parkinson’s disease (PD) duration, Hoehn-Yahr stage, and levodopa equivalent daily dose (LEDD) combined with serum GDNF; Combination 2: PD duration, Hoehn-Yahr stage, LEDD, and alcohol consumption combined with serum GDNF; Combination 3: PD duration, Hoehn-Yahr stage, LEDD, alcohol consumption, sex, age, education, high blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking combined with serum GDNF. GDNF: Glial cell derived neurotrophic factor; LEDD: levodopa equivalent daily doses; MMSE: min-mental state examination; MoCA: Montreal cognitive assessment; PD: Parkinson’s disease.