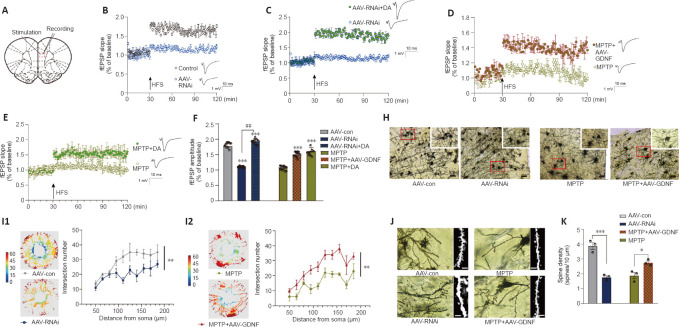
Figure 6.
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) altered long-term potentiation (LTP), mediated by dopamine (DA) level, dendritic spine density, and morphology of the prefrontal cortex (PFC).
(A) Sketch map of the electrophysiology of a PFC slice. (B) GDNF loss decreased LTP, corresponding to the greater decrease in the field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) slope compared with that of the control group, which was evoked by a reduction in the extracellular DA level. (C) LTP was facilitated again by supplementation of DA, which increased medial prefrontal excitability. (D) LTP was measured as a decrease in the slope of the fEPSP in the PFC of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) mice. However, with sufficient GDNF (the MPTP + adeno-associated virus (AAV)-GDNF group), the LTP situation improved. (E) Additional DA in the brain slice of the MPTP group exhibited similar fEPSP recovery to that of the MPTP group, which indicated that DA supplementation successfully evoked LTP in the PFC slice of MPTP rats. (F) Significant differences in the fEPSP amplitude among groups. Compared with the AAV-control (con) group, fEPSP amplitudes in the AAV-RNAi and AAV-RNAi + DA groups were higher (***P < 0.001). Compared with the AAV-RNAi group, the DA supplementation group had higher amplitudes (##P < 0.01). Slices were preincubated for 40 minutes with artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) and continually perfused during the experiment. LTP (% fEPSP) was induced by high-frequency stimulation HFS (100 Hz, 1 second). Data were analyzed using Student’s t-tests. (H) Golgi staining of pyramidal neurons in the PFC (Cg1 and PrL areas) showed alterations in dendritic length, branching, and morphology. Scale bars: 100 μm. (I1) In the same set of dendrites, Sholl analysis showed that the number of dendrites significantly decreased in the GDNF loss (AAV-RNAi) group. (I2) Sholl analysis was used to compare the number of intersections in the MPTP and GDNF + MPTP groups. (J, K) Dendritic spine density and morphology. Scale bars: 10 μm. As seen with the total spines, GDNF-loss rats and MPTP rats had reduced spine density. In contrast, spine density was significantly elevated in GDNF + MPTP rats. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). Data are expressed as means ± standard deviations (n = 3–5). AAV: Adeno-associated virus; fEPSP: field excitatory postsynaptic potentials; HFS: high-frequency stimulation; MPTP: 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.