Figure 7.
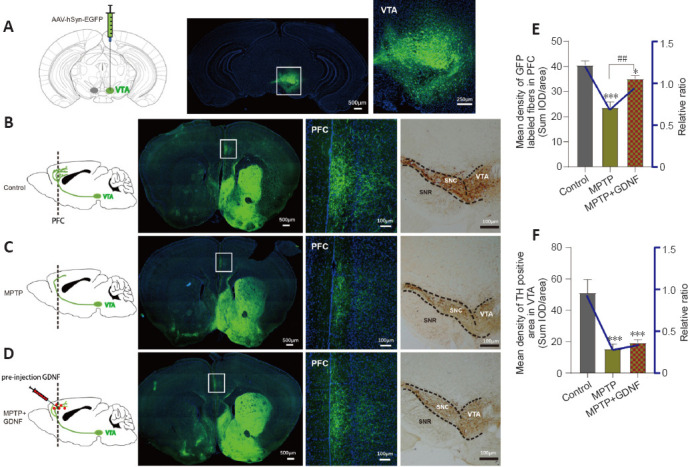
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) decreases the loss of dopaminergic axons from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) in the prefrontal cortex (PFC).
(A) Diagram of a sagittal mouse slice depicting the site of the anterograde viral injection site and photomicrographs of the injected site in the VTA. (B–D) Specificity to express green fluorescence protein (GFP) in the PFC dopaminergic fibers from the VTA in different groups. Left, diagram of dopaminergic axon density in the PFC. Right, GFP tracking derived from the VTA neurons and expanded images of the regions of interest (white rectangle, PFC). Scale bars: 100 μm. (E, F) Statistics of the GFP-positive axons in the PFC of different groups. The graph shows the mean density of GFP fibers, which indirectly indicates the number and density of fibers from the VTA. Data are expressed as means ± standard deviations (n ≥ 3). ***P < 0.001, vs. control group; ##P < 0.01, vs. 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) group (Mann-Whitney U test). AAV: Adeno-associated virus; EGFP: enhanced green fluorescent protein; GFP: green fluorescent protein; hSyn: human synapsin I; MPTP: 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.
