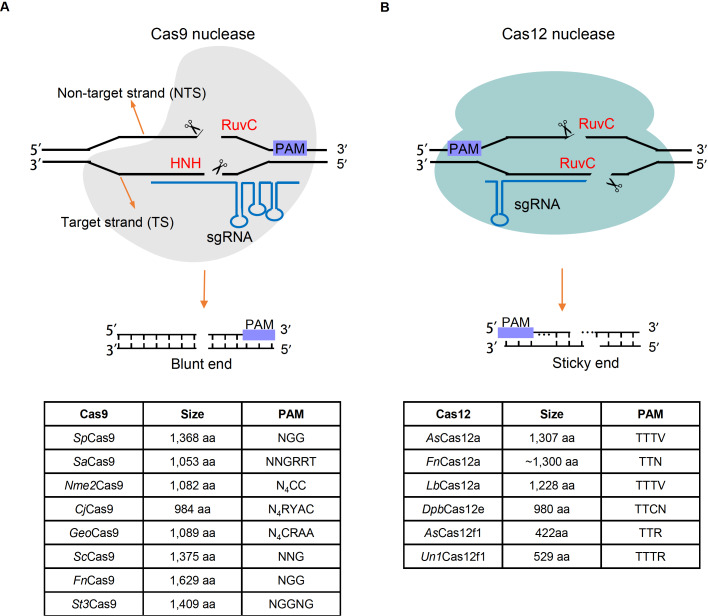
Figure 2 .
Two main Cas nucleases for genome editing
Cas nucleases are guided by sgRNA to the target site by forming an “R loop”. (A) Cas9 nucleases use the HNH domain to cleave the target strand and RuvC domain to cleave non-target strand both upstream PAM. Cas9 nucleases tend to generate blunt ends. (B) Unlike Cas9, Cas12 nucleases use only the RuvC domain to cleave both target and on-target strand downstream PAM, and Cas12 nucleases generate sticky end. Currently-developed Cas9 and Cas12 nucleases with their size and PAM are displayed on the bottom.