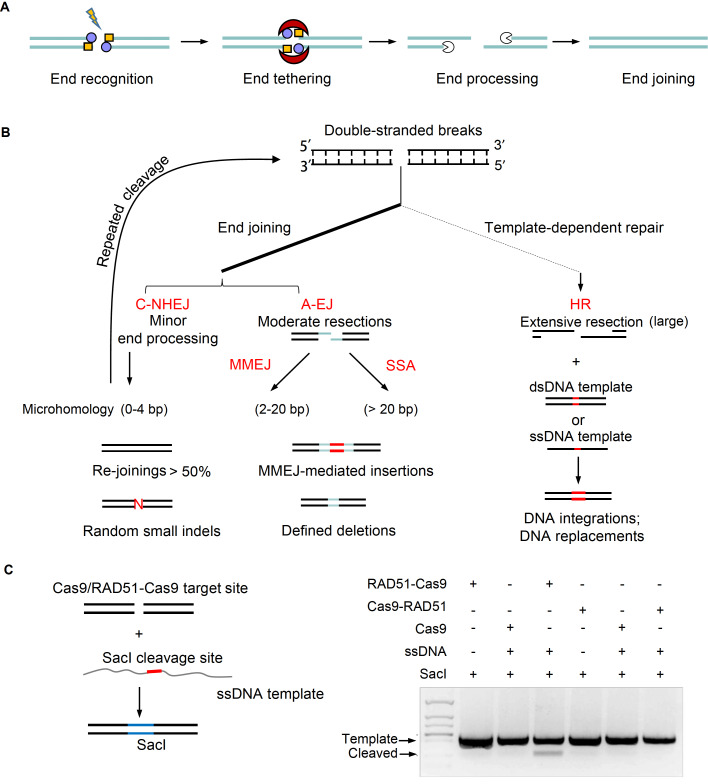
Figure 3 .
DSB repair pathways involved in genome editing
(A) General steps for DSB repair. End recognition, end tethering, end processing, and end joining. (B) DSB repair pathways for genome editing. DSB repairs are mainly subtyped into end-joining and template-dependent repair. C-NHEJ directly joins two broken ends with small indels in the final products due to limited end processing. Note that more than 50% of products generated by C-NHEJ are re-joinings and will undergo several cycles of repeated cleavage until the formation of indels. The process of end-joining may use homology on the broken ends to generate defined deletion or insertions. Due to the length of the homology, homology length from 2 to 20 bp is recognized as MMEJ and more than 20 bp is recognized as SSA. Template-dependent repair needs extensive resection and uses dsDNA template or ssDNA template. (C) RAD51-Cas9 enhances ssDNA integration. ssDNA template with a SacI cleavage site and homologous arm is co-transfected with Cas9 or RAD51-Cas9. If integration occurs, the DNA bands can be cleaved by the restriction enzyme SacI.