Figure 1.
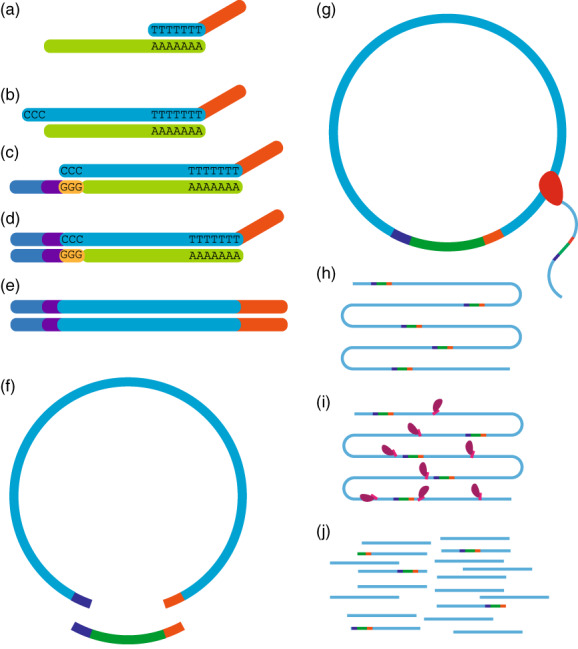
Design overview of Smar2C2.
(a) cDNA is generated with a template‐switching reverse transcriptase using extracted RNA (light green) and a poly‐dT primer (light blue) with an adaptor (orange) (b). (c) A template‐switching oligo containing an adaptor (blue) and unique molecular identifier (UMI) (purple) is bound to the deposited cytosines and used to add the second adaptor and UMI to the cDNA (d). The final construct (e) is circularized using a linker (dark green) (f) and amplified using rolling circle amplification (g). Rolling circle amplification generates a linear strand of repeating segments (h), and Tn5 is used to generate a final library for sequencing (i). This places the transcription start site (TSS), identifying adaptor and UMI in variable locations within the read (j), allowing for them to be sequenced and extracted bioinformatically.
