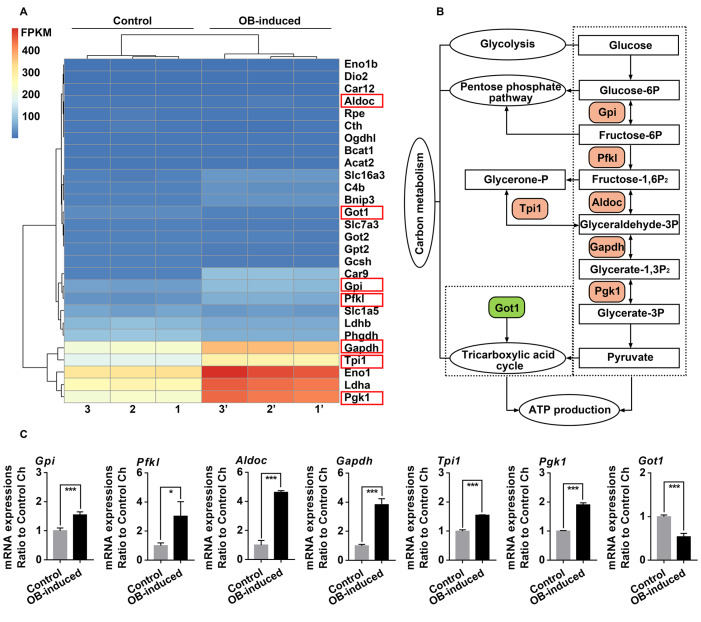
Figure2 .
Osteoblasts induce alterations in the mRNA expressions of genes related to glucose-derived ATP perturbations in chondrocytes
(A) Heatmap from RNA sequencing showing the change of genes related to carbon metabolism pathway in chondrocytes after 3 days of co-culture with osteoblasts. Three pairs of samples, i.e., samples 1 and 1’, samples 2 and 2’, and samples 3 and 3’, were obtained from three independent mother cells (n=3). Genes in red boxes are significantly changed in terms of carbon metabolism. (B) Schematic diagram showing the crucial steps and key enzymes of the flux of glucose-derived carbons for ATP production in chondrocytes. Tree diagram was obtained from the online KEGG enrichment analysis. Color-labeled candidates are changed in osteoblast-induced chondrocytes in this study. (C) qRT-PCR confirmed the gene expression of key enzymes in the flux of glucose-derived carbons for ATP production in chondrocytes after 3 days of co-culture with osteoblasts. Six enzymes, including Gpi, Pfkl, Aldoc, Gapdh, Tpi1, and Pgk1, were upregulated, while Got1 was downregulated. Hprt was used as the internal control. mRNA expression is presented as the fold change ratio to the control chondrocytes. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments (n=3). The data in C are presented as the mean±SD. Significant differences were observed in the control chondrocytes. *P<0.05, **P<0.025, and ***P<0.01. Ch, chondrocytes; OB, osteoblasts.