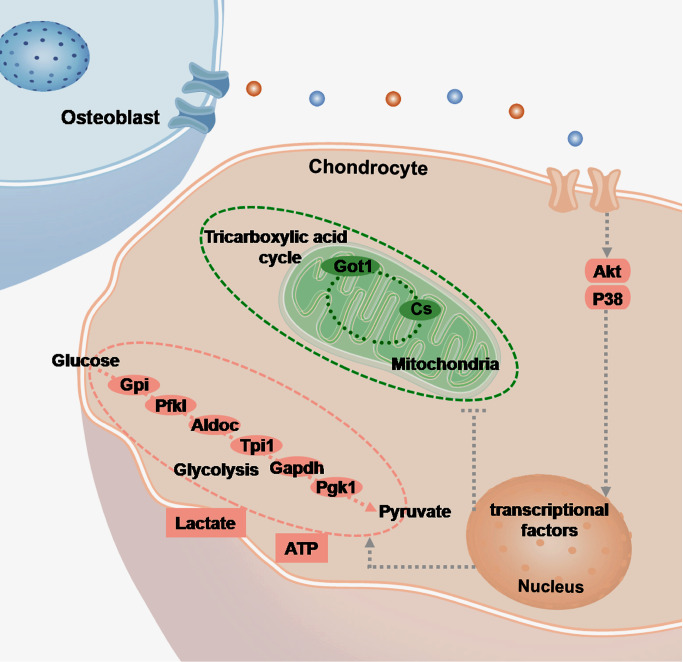
Figure5 .
Schematic diagram illustrating the changes in the flux of glucose-derived carbons for ATP production in chondrocytes induced by osteoblasts
Osteoblasts activate Akt and P38 signaling pathways in chondrocytes via noncontact communication (shown in pink rounded-rectangle boxes). The grey dotted lines point to the possible downstream targets identified by existing studies. Dramatic changes in the flux of glucose-derived carbons for ATP production are induced. The expressions of glycolytic enzymes (Gpi, Pfkl, Aldoc, Tpi1, Gapdh, and Pgk1) are increased, while the expressions of enzymes in the TCA cycle (Got1 and Cs) are decreased (shown in pink and green ellipses, respectively). In osteoblast-induced chondrocytes, although the TCA cycle seems to be suppressed (encircled with green dotted lines), glycolysis is promoted (encircled with pink dotted lines); thus, intracellular ATP level is significantly increased (shown in pink rectangular boxes).