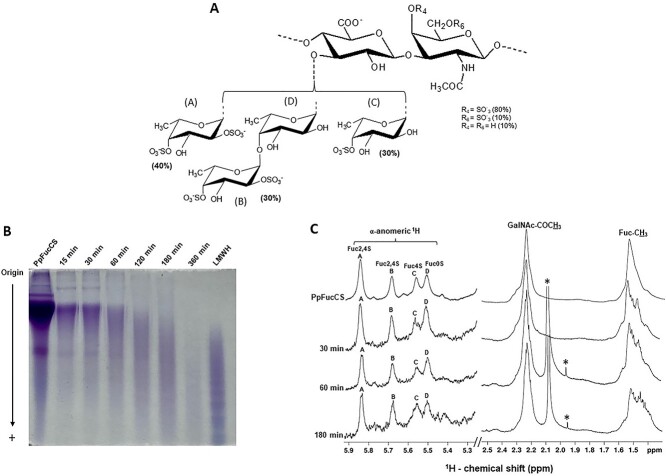
Fig. 1.
Free-radical depolymerization of PpFucCS by copper-based fenton method. A) Structural representation of PpFucCS, showing a chondroitin sulfate backbone of alternating GalNAc and GlcA in repeating disaccharide units of [→3)-β-GalNAc-(1 → 4)-β-GlcA-(1→]n, where the GalNAc units are mostly 4-sulfated (80%), 6-sulfated (10%), or nonsulfated (10%). The GlcA units are substituted at the C3 position by 3 types of α-Fuc branches: 40% [Fuc2,4S-(1→] (A unit in NMR), 30% [Fuc2,4S-(1 → 4)-Fuc-(1→] (B → D units in NMR), and 30% [Fuc4S-(1→] (C unit in NMR), where S = SO3−. B) Optimization of free-radical depolymerization reaction conditions of PpFucCS achieved by copper-based Fenton method—2 mg/mL of PpFucCS depolymerized by 0.02 mM copper (II) acetate and 200 mM H2O2 for different durations: 15 min, 30 min, 60 min, 120 min, 180 min, and 360 min. MW distribution of the depolymerized reaction mixture was analyzed by PAGE using the molecular markers: LMWH, and native PpFucCS. C) 1D 1H NMR spectra were recorded in D2O, at 50 °C, on a 500 MHz Bruker NMR instrument for the native PpFucCS and its depolymerized reaction mixture at 3 time points (30 min, 60 min, and 180 min). The NMR signals corresponding to characteristic fucosyl branches in the α-anomeric region (δH expansion 5.9–5.3 ppm) of the depolymerized products obtained at different time points are labeled on top of the spectral stack as A (Fuc2,4S), B (Fuc2,4S), C (Fuc4S), and D (Fuc0S). Upfield region (δH expansion 2.5–1.4 ppm) diagnostic of 1H signals from the protons of GalNAc-COCH3 and of Fuc-CH3 shows the characteristic methyl peaks from native PpFucCS and oligosaccharide mixtures. The signals indicated with asterisks are from solvent.