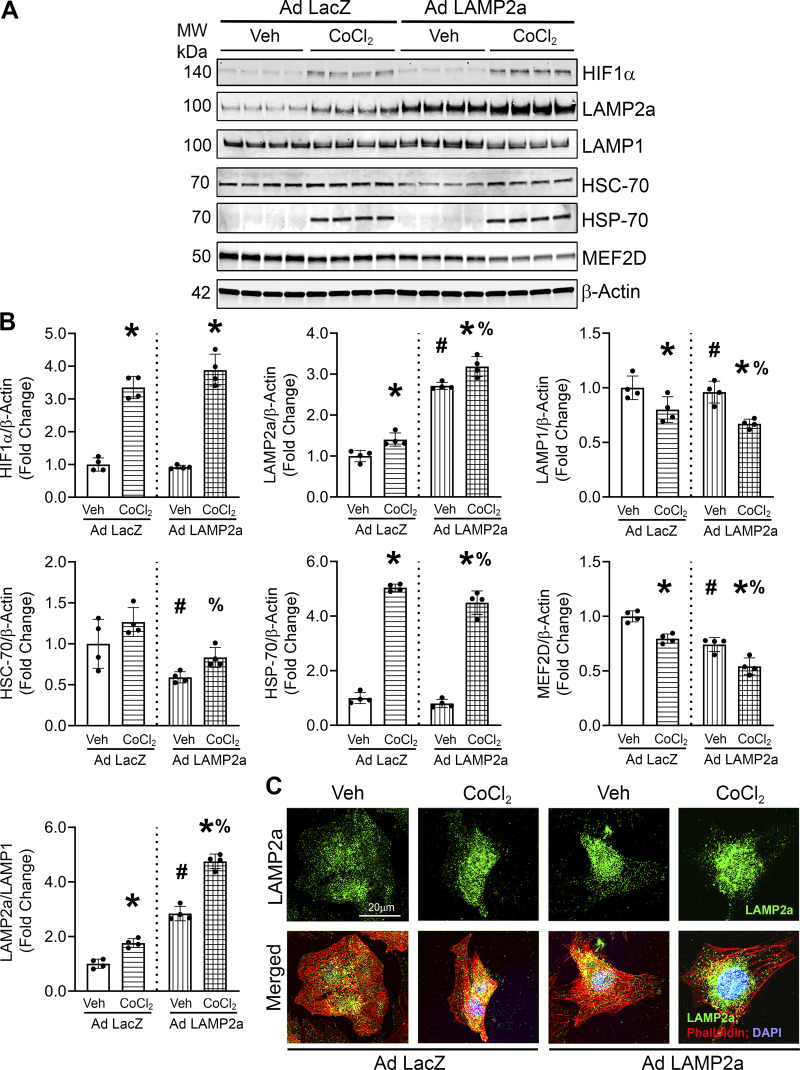
Figure 3.
Lysosome associated membrane protein receptor 2a (Lamp2a) overexpression increased chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) marker proteins in CoCl2-treated cardiomyocytes. Lamp2a- and LacZ-overexpressing cardiomyocytes were treated with CoCl2 for 48 h to induce hypoxia, or a vehicle (Veh) control. A: immunoblot analyses of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α), LAMP2a, lysosome associated membrane protein receptor 1 (LAMP1), heat shock cognate 70 (HSC-70), heat shock protein 70 (HSP-70), and myocyte enhancer factor 2D (MEF2D) were carried out. B: bar graphs show the band densitometry of the immunoblots. The protein levels were normalized to β-actin level which was used as the loading control. C: immunofluorescence studies were performed to determine if LAMP2a was localized into lysosomal punctate structures. Cardiomyocytes were stained with an anti-LAMP2a antibody to detect LAMP2a localization (green), Phalloidin-stained actin (red) and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue); n = 2 wells/group. LAMP2a fluorescence was largely limited to cytosolic, perinuclear punctate structures consistent with lysosomal staining and showed similar changes to those found by immunoblotting across the different treatments. Each image is a representative of 6–8 individual images collected under identical conditions using an objective of ×60. Results of immunoblots are means ± SD from four independent groups. (n = 4); *P < 0.05: difference between CoCl2 treatment within infection group; #P < 0.05: difference between infection within Veh groups; and %P < 0.05: difference between CoCl2-treated groups.