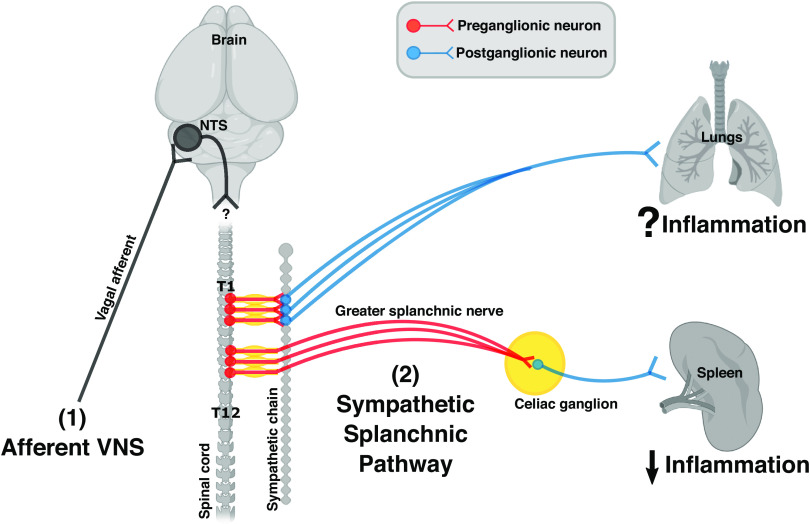
Figure 2.
The organization of sympathetic innervations in the spleen and the lungs. Cell bodies of sympathetic preganglionic neurons illustrated here (red) are in the thoracic spinal cord between level T1 and T12. Axons from preganglionic neurons (located in T1 to T5) synapse with postganglionic neurons (blue) at the paravertebral ganglia within the sympathetic chain. Axons from these postganglionic neurons travel to and innerve the lungs. The immunomodulatory effect of this pathway remains unknown. In contrast, axons from preganglionic neurons (located in T6 to T8) enter the greater splanchnic nerve, synapse with postganglionic neurons at the celiac ganglion, and innervate the spleen. Activation of this sympathetic splanchnic pathway is known to suppress inflammation in the spleen. [Image created with BioRender.com and published with permission.]