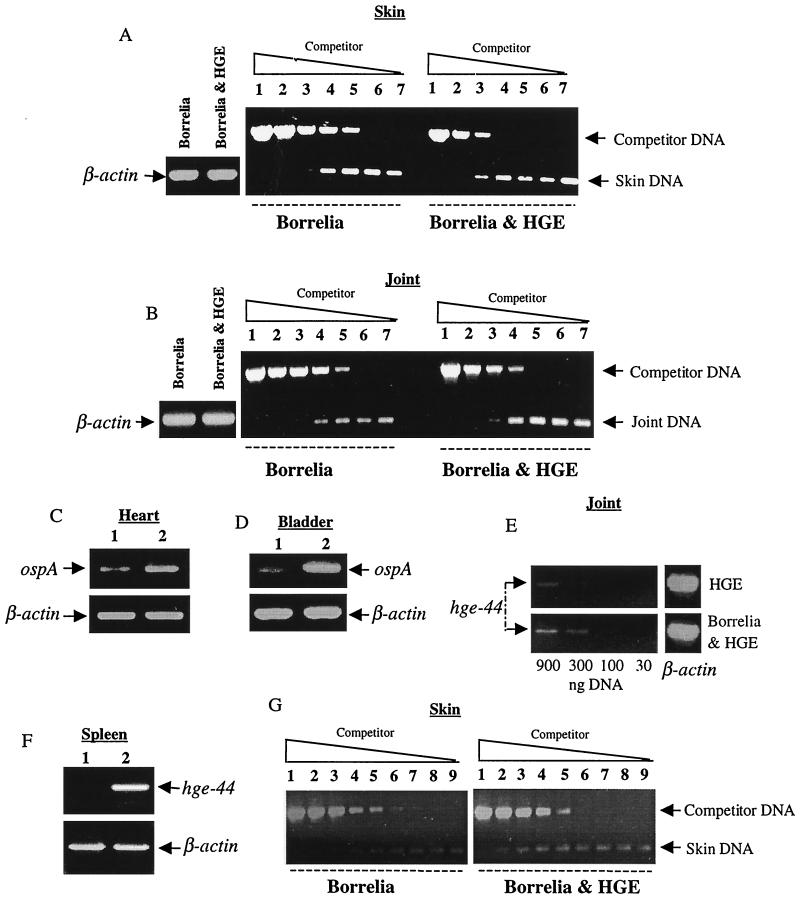
FIG. 2.
Coinfection elevates levels of the HGE agent and B. burgdorferi at 2 weeks. DNAs from various tissues of the five mice in each group were pooled and analyzed by PCR with primers specific for either B. burgdorferi ospA or hge-44. Skin (A) and joints (B) were analyzed by competitive PCR with primers specific for B. burgdorferi bbk50 (also known as p37) (28, 31). Lanes 1 through 7 contain 10-fold dilutions (87 to 0.000087 fg) of competitor DNA. Primers specific for ospA were used to amplify heart (C) and bladder (D) DNAs from singly B. burgdorferi-infected (lanes 1) and coinfected (lanes 2) mice. Joint DNA (E) was analyzed by dilutional PCR for hge-44. Splenic DNA (F) from mice either infected with HGE only (lane 1) or coinfected (lane 2) was analyzed for hge-44. Skin DNA (G) from mice infected for 2 months was analyzed by competitive PCR with primers specific for B. burgdorferi bbk50. Lanes 1 through 9 contain fourfold dilutions (0.137 to 0.000002 fg). PCR for β-actin was performed with 1 μg of total DNA to ensure that equal amounts of DNA were used. Five separate experiments were performed, with similar results. Results from one of these five representative experiments are presented.