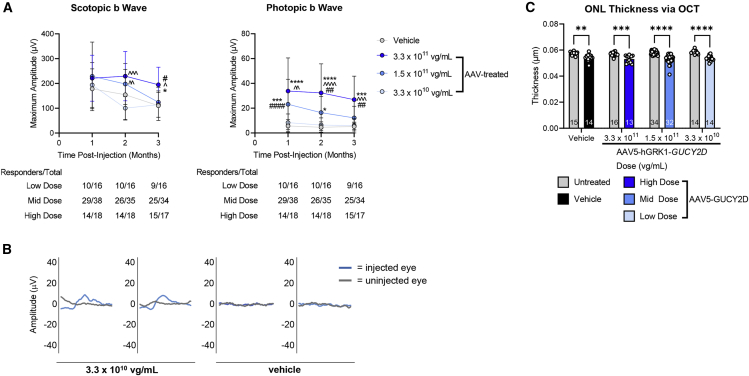
Figure 4.
Hybrid study evaluates safety and efficacy of AAV5-hGRK1-GUCY2D in subretinally injected GC1KO mice
(A) Rod-mediated (scotopic) and cone-mediated (photopic) function were evaluated in GCDKO mice for 3 months after injection with a low (3.3 × 1010 vg/mL), mid (1.5 × 1011 vg/mL), or high (3.3 × 1011 vg/mL) concentration of the vector. This corresponds to doses of 3.3 × 107, 1.5 × 108, and 3.3 × 108 vg/eye, respectively. (B) Cone mediated b wave amplitudes were significantly improved after treatment with the mid- and high-dose vector. Although significant improvements were not observed at the low dose, genuine waveforms were present in the majority (9 of 16) of treated animals. Two representative waveforms from low-dose vector-treated and vehicle-treated mice reflect this observation. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 versus vehicle; ˆp < 0.05, ˆˆp < 0.01, ˆˆˆp < 0.001, ˆˆˆˆp < 0.0001 versus low dose; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, ####p < 0.0001 versus mid dose, as determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test analysis. (C) There was no significant difference in mean outer nuclear layer (ONL) thickness between vehicle-treated and AAV5-hGRK1-GUCY2D-treated eyes at any dose, indicating that the test article was well tolerated. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, as determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test analysis.