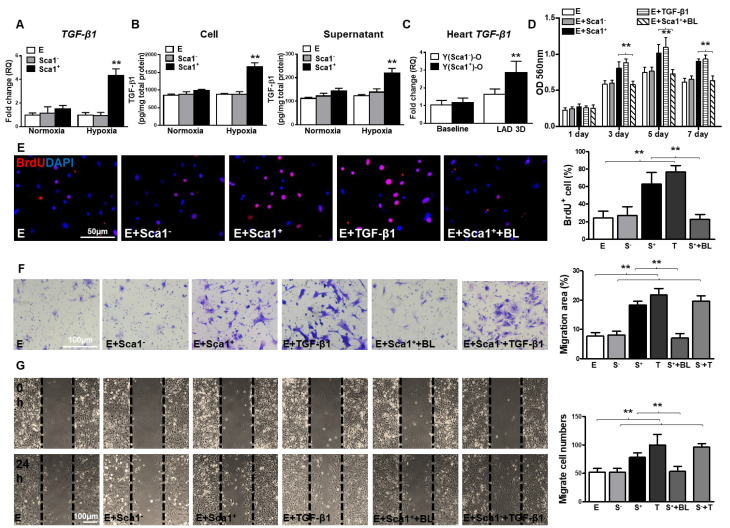
Figure 5.
BM Sca-1+ cells increased proliferation and migration of EPDCs through TGF-β1 signaling. Epicardial-derived cells (EPDCs, abbreviated as E), bone marrow (BM) Sca-1+ and Sca-1- cells were isolated and subjected to normoxia and hypoxia (0.1% O2) conditions. (A) Higher expression levels of TGF-β1 mRNA were found in BM Sca-1+ cells than in EPDCs and Sca-1- cells under hypoxia conditions for 72 h. (B) TGF-β1 homodimer secretion in EPDCs, BM Sca-1+ and Sca-1- cell lysate and culture medium under normoxia and hypoxia conditions for 72 h was quantified by ELISA. (C) TGF-β1 mRNA expression was measured in the Y(sca-1+)-O and Y(sca-1-)-O chimeric hearts at baseline and in the infarcted area at 3 days post-MI. Epicardial-derived cells (EPDCs, abbreviated as E) were co-cultured with BM Sca-1- cells (S-), Sca-1+ cells (S+), TGF-β1 (T, 5 ng/mL), Sca-1+ cells with TGF-β1 blocking antibody (S++BL, 1 µg/mL) or Sca-1- cells with TGF-β1 (S-+T) under hypoxia conditions. The following assays were conducted in EPDCs: (D) MTT assay measured cell proliferation; (E) EPDCs, co-cultured with BM Sca-1+ cells or Sca-1- cells under normoxia and hypoxia conditions for 72 h, were pulse-chased with BrdU (10 µM) for labeling of proliferative cells; (F) transwell and (G) wound-scratch assays measured migration areas and number of EPDCs after co-culture for 24 h, respectively. Insufficiency of Sca1- cells on EPDC migration can be rescued by TGF-β1, and EPDC migration was restored to a level comparable with that of the Sca-1+ cell- or TGF-β1-treated groups. n=6/group, mean ± SD; **P<0.01. BrdU: bromodeoxyuridine; MTT: 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide.