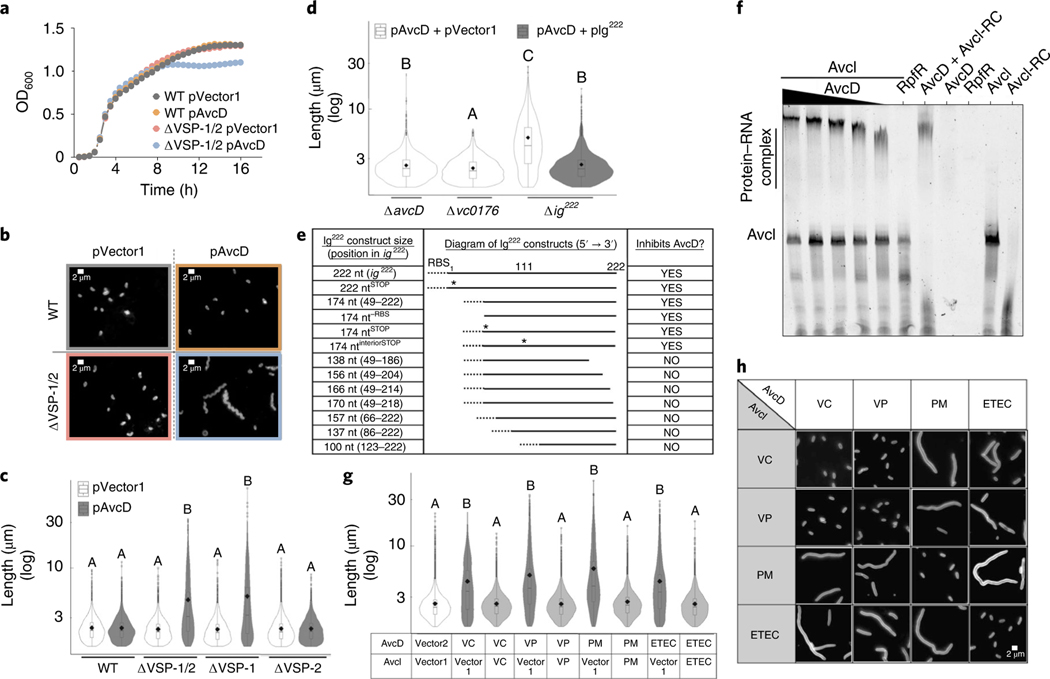
Fig. 1 |. AvcD-induced filamentation is inhibited by sRNA Avci.
Growth curves (a) and representative images (b) of WT El Tor V. cholerae and ΔVSP-1/2 strains expressing avcD from a Ptac-inducible plasmid (pAvcD) or an empty vector control (pVector1). Cells were stained with FM4–64 before imaging. Scale bar, 2 μm. This experiment was repeated at least three times. c, Cell length distributions of WT V. cholerae and VSP island mutants expressing pAvcD or pVector1. d, Cell length distributions of VSP-1 gene locus mutants expressing pAvcD in combination with either pIg222 or a vector control (pVector2). e, Table reporting the capacity of various ig222 Ptac-inducible constructs to prevent AvcD-induced cell filamentation when expressed in combination with pAvcD in Δig222 V. cholerae. Dotted line denotes a non-native RBS, ‘*’ indicates a putative start codon mutated to a stop. f, An AvcD–AvcI complex formed in an AvcD concentration-dependent manner as determined by EMSA. Trace quantities of non-specific binding of AvcD to the AvcI reverse complement (AvcI-RC) were observed. This experiment was repeated at least three times, yielding similar results. g, Cell length distributions of E. coli co-expressing Ptac-inducible plasmids encoding avcD homologues and their cognate avcI or vector controls. VC, Vibrio cholerae; VP, Vibrio parahaemolyticus; PM, Proteus mirabilis; ETEC, E. coli ETEC. h, Representative images of E. coli co-expressing various combinations of Ptac-inducible plasmids encoding homologues of avcD and avcI. Scale represents 2 μm. Error bars represent s.e.m. from three biological replicates. All violin plots represent ~1,000–3,000 cells measured per strain (n = 3 biological samples) with summary statistics: mean (diamonds), median (horizontal black line), interquartile range (box) and data below and above the interquartile range (vertical lines). Different letters indicate significant differences using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post-hoc test (c and d) or to two-sided Dunnett’s post-hoc test (g) against the control strain (pVector1 + pVector2) at P < 0.05.