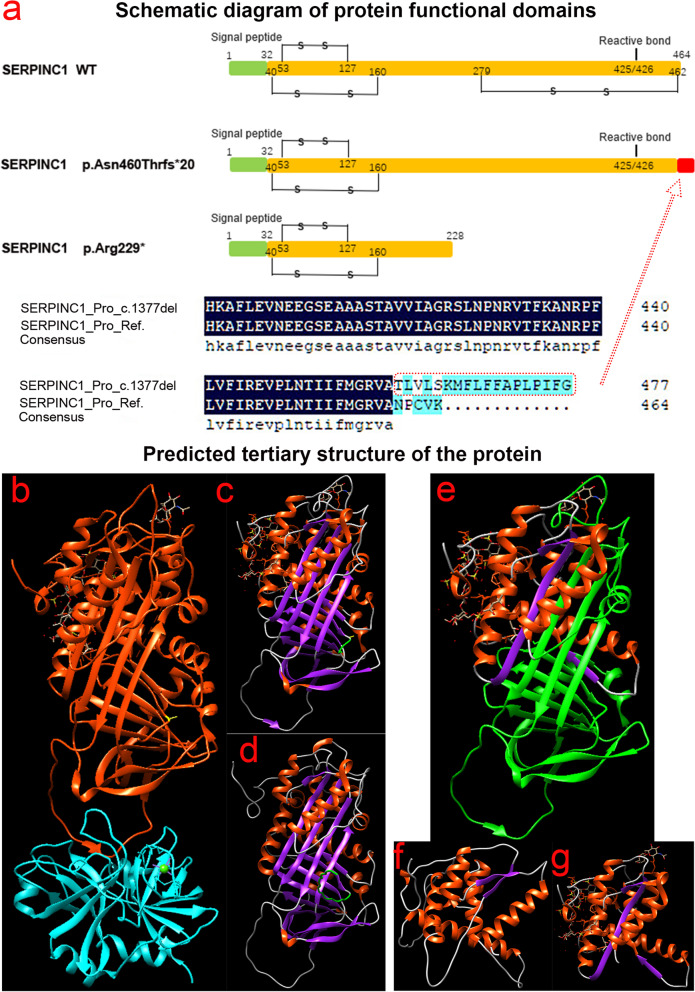
Fig. 5.
Prediction of structures of antithrombin (AT) protein mutants. (a) Schematic representation of functional domains of AT proteins and their variants. (b) Three-dimensional crystal structure diagram of AT protein versus coagulation factor IX (FIX) in Swiss-model database; red represents AT protein, green FIX protein, and yellow Asn460 (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/P00740?template=3kcg). (c) Swiss-model prediction of the three-dimensional structure of the Asn460Thrfs*20 mutant, with the yellow site represents Asn460 and the green sequence as the amino acid sequence missing from the frameshift mutation. (d) The three-dimensional structure of the Asn460Thrfs*20 mutant was predicted by Alphafold2 software, and the green sequence was the amino acid sequence that was generated after frameshift. (e) The sequence in green is the sequence deleted by the nonsense mutation Arg229*. (f) The deletion protein structure of the nonsense mutation Arg229* resulted in the loss of the domain interacting with FIX (Ala414 site). (g) Alphafold2 predicts the tertiary structure of a truncated protein with the nonsense mutation Arg229*