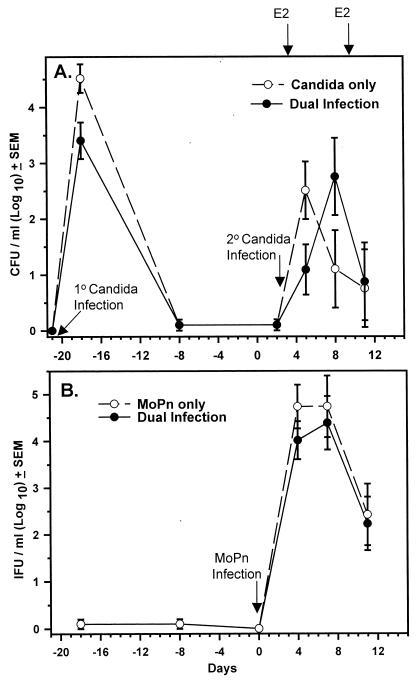
FIG. 2.
Ability of a MoPn genital infection to influence the fungal burden of a secondary Candida vaginal infection. Mice were inoculated with Candida (primary [1°] infection; day -21) followed by progesterone treatment (day -7) and inoculated with MoPn on day 0. On day 2, mice were treated with estrogen (E2) and inoculated with Candida a second time (secondary [2°] infection). Controls included mice inoculated with MoPn or Candida alone (day 2) following identical hormone treatments and primary Candida infection. (A) Vaginal Candida burden (CFU). (B) Genital tract Chlamydia burden (IFU, inclusion forming units). Each data point represents the mean ± standard error of the mean of eight mice per group. No significant differences were found among groups by two-way analysis of variance.