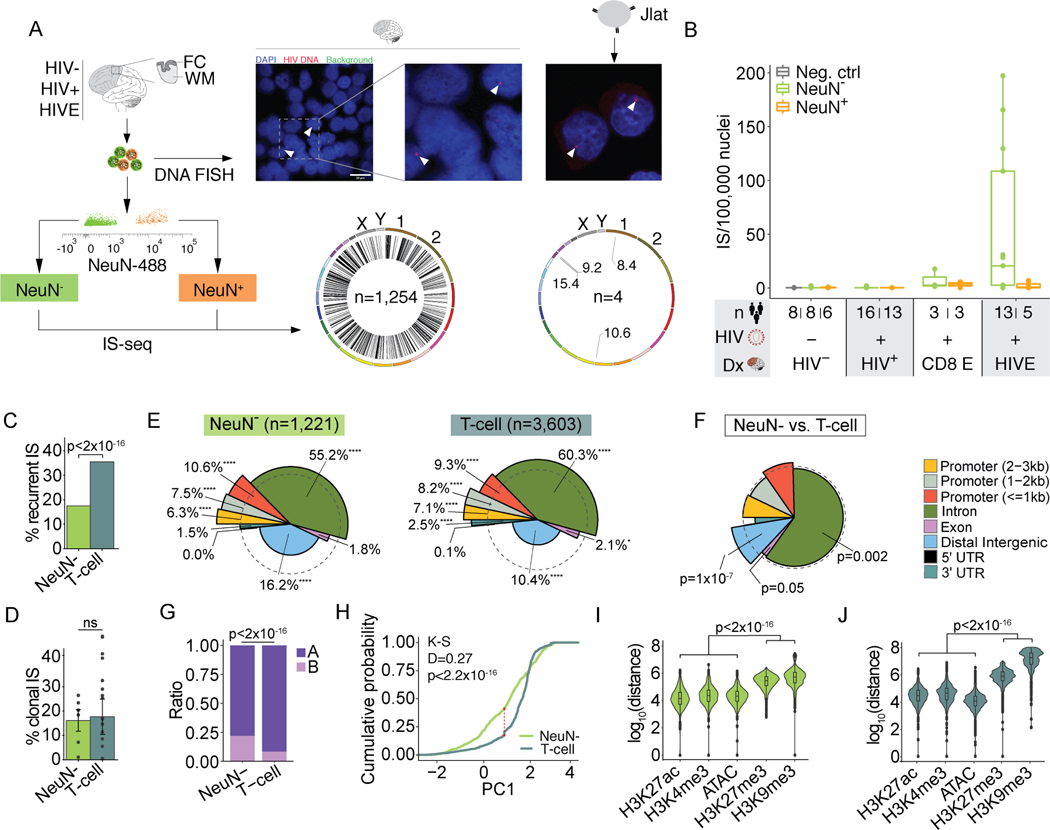
Figure 4. Genomic and epigenomic features of IS in human brain.
(A) Representative FANS plot for sorting of NeuN+ and NeuN- nuclei for FC/WM IS-seq and JLat cells for comparison. HIV DNA FISH from HIVE nuclei (left) and JLat cells (right), arrowheads indicate positive signal. Genome-wide IS circos plots (left, brain n=1,254 IS; right, 4 JLat clones n=4 IS). (B) Boxplots show number of IS/100,000 nuclei (y-axis). Diagnosis (Dx) is indicated on the x-axis. CD8 E, CD8 encephalitis; Neg. Ctrl., uninfected Jurkat cell DNA. (C-D) Percent of recurrent (C) and clonal (D) IS for NeuN- and in vivo T-cell IS54–59. Significance testing by chi-square (C) or two-way ANOVA (D). (E) Spie charts comparing proportional IS distribution across 8 genomic features as indicated. Dashed circle demarcates equal (expected) proportions and % denote the IS feature percent. Chi-square test. * 0.01 < p < 0.05, ** 0.001 < p < 0.01, *** 0.0001 < p < 0.001, **** p<0.0001 (Bonferroni multiple comparison factor x 8, significance threshold at p = 0.00625) (F) Spie chart comparing NeuN- IS distribution to T-cell. Chi-square test. (G) Bar plot showing the proportion of NeuN- or in vivo T-cell IS found in A/ B compartments in HIV- microglia or uninfected Jurkat T-Cell Hi-C data respectively. P, Chi-square. (H) Empirical cumulative distribution function graph of NeuN- and T-cell IS for PC1 values. NeuN- IS are compared to HIV- microglia Hi-C data and T-cell IS are compared to uninfected Jurkat Hi-C (two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, red line Dmax). (I-J) Violin plots showing distance between NeuN- or T-cell IS and the nearest corresponding peak from NeuN- or Jurkat specific open and repressive chromatin marks. Kruskall Wallis rank sum tests. See also Figure S6.