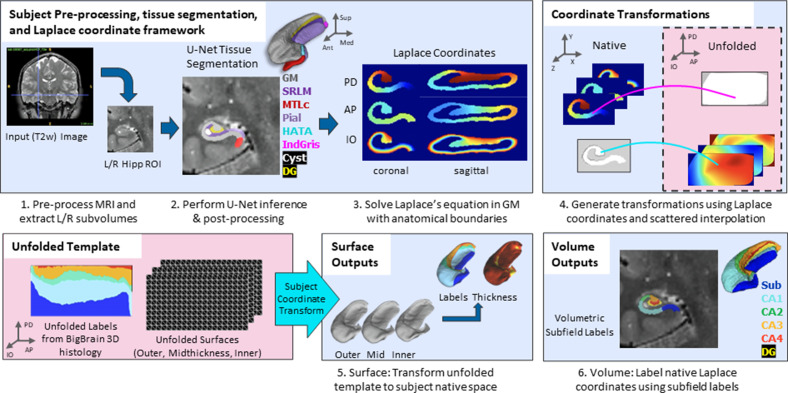
Figure 1. Overview of HippUnfold pipeline.
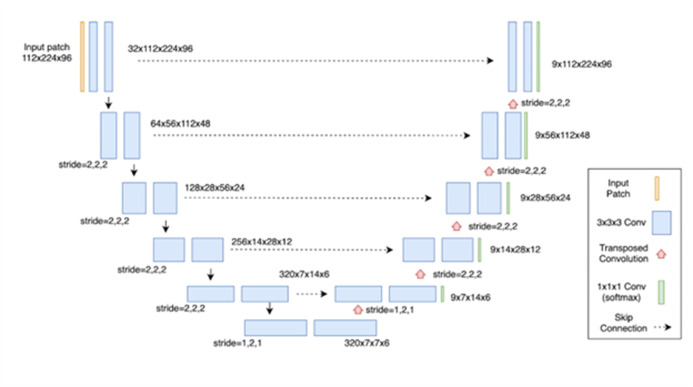
First, input MRI images are preprocessed and cropped around the left and right hippocampi. Second, a U-Net neural network architecture (nnUNet; Isensee et al., 2021) is used to segment hippocampal grey matter (GM), the high-myelinated stratum radiatum, lacunosum, and moleculare (SRLM), and structures surrounding the hippocampus. Segmentations are post-processed via template shape injection. Third, Laplace’s equation is solved across the anterior-posterior (AP), proximal-distal (PD), and inner-outer (IO) extent of hippocampal GM, making up a geodesic coordinate framework. Fourth, scattered interpolants are used to determine equivalent coordinates between native Cartesian space and unfolded space. Fifth, unfolded surfaces with template subfield labels (DeKraker et al., 2020) are transformed to subjects’ native folded hippocampal configurations. Morphological features (e.g. thickness) are extracted using Connectome Workbench (Glasser et al., 2013) on these folded native space surfaces. Sixth, volumetric subfields are generated by filling the voxels between inner and outer surfaces with the corresponding subfield labels. Additional details on this pipeline can be found in the Materials and methods.