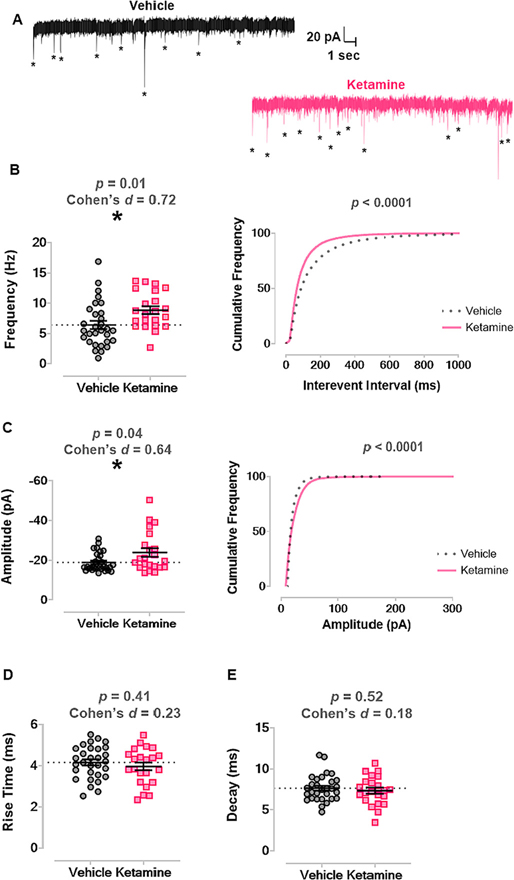
Fig. 6. Neonatal ketamine exposure significantly increased frequency and amplitudes of mEPSCs at later (PND30 and PND40) developmental stages.
A. Left panel shows representative trace of mEPSCs recorded from a vehicle treated mouse in later juvenile development. Right panel shows representative trace of mEPSCs from a mouse treated with ketamine as a neonate. Asterisks mark mEPSCs. B. Mice treated with ketamine as neonates (n = 12 mice, n = 22 neurons) had higher average frequency of mEPSCs compared to mice that received vehicle (n = 11 mice, n = 30 neurons) (left panel) and a leftward shift in mEPSC interevent interval (right panel). C. Neonatal ketamine caused an increase in average amplitude of mEPSCs compared to vehicle (left panel) and a rightward shift in cumulative frequency of mEPSC amplitude (right panel). D. There was no change in mEPSC rise time between groups. E. There was no change in mEPSC decay between groups.
mEPSC, miniature excitatory postsynaptic current; PND, postnatal day.