Figure 1.
Molecular characterization of spinal Kcnip2 neurons
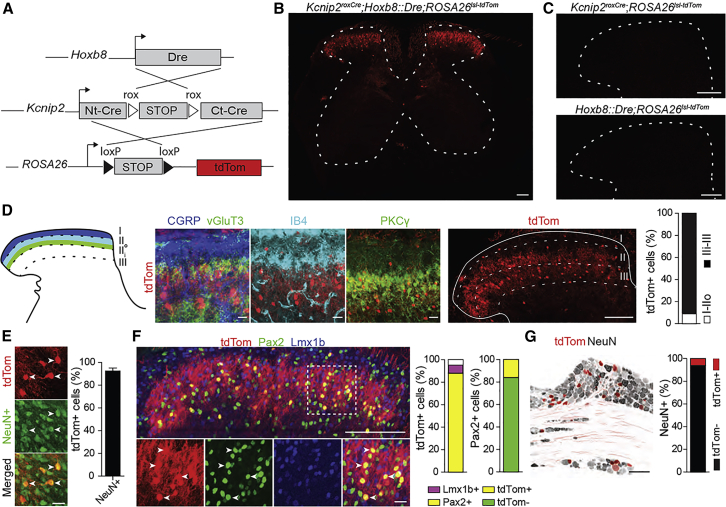
(A) Desired recombination events in Kcnip2roxCre;Hoxb8::Dre;ROSA26lsl-tdTom mice.
(B) TdTom expression in transverse section of the lumbar spinal cord of Kcnip2roxCre;Hoxb8::Dre;ROSA26lsl-tdTom triple transgenic mice.
(C) Same as (B), but in mice lacking either the Kcnip2roxCre or Hoxb8::Dre transgene. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(D) Kcnip2-tdTom neurons (red) in transverse sections of the lumbar spinal cord relative to lamina-specific markers CGRP (blue), vGluT3 (green), IB4 (cyan), and PKCγ (green). Six sections from two mice. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(E) Kcnip2 cells co-expressing the neuronal marker NeuN (green). n = 4 sections from three mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. Mean ± SEM.
(F) Co-expression of tdTom (red) with Pax2 (green; inhibitory neurons) and Lmx1b (blue; excitatory neurons). n = 7 sections from two mice; Scale bars: 100 μm (top), 20 μm (bottom). Bar charts: n = 11 sections from three mice.
(G) Lumbar DRG with Kcnip2 neurons (red) and NeuN staining (gray). n = 6 sections from two mice. Scale bar, 100 μm.