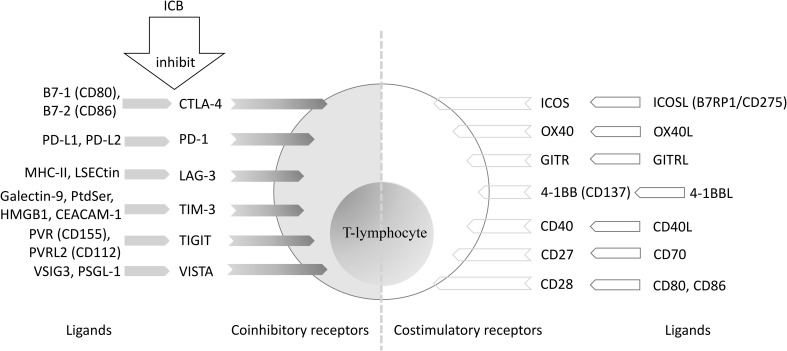
Figure 1.
T lymphocyte-associated co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory molecules. ICB, immune checkpoint blockade; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand-1; PD-L2, programmed cell death ligand-2; MHC: major histocompatibility complex; LSECtin, liver and lymph node sinusoidal endothelial cell C-type lectin; LAG-3, Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3; PtdSer, phosphatidylserine; HMGB1, High Mobility Group Protein 1; CEACAM-1, carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule-1; TIM-3, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-containing molecule 3; PVR: poliovirus receptor; PVRL2, poliovirus receptor-related protein 2; TIGIT, T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domains; VISTA, V-domain immunoglobulin suppressor of T cell activation; PSGL-1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1; VSIG3, V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing 3; ICOS, inducible T-cell co-stimulator; B7RP1, B7-related protein 1; GITR, glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor; 4-1BB, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9.