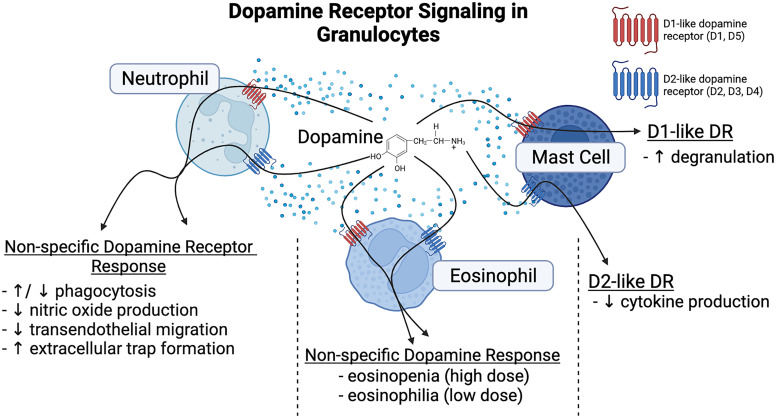
Fig. 4.
Dopamine receptor signaling in granulocytes. Current knowledge of the immunomodulatory effects of dopamine signaling in neutrophils, eosinophils, and mast cells is summarized. In neutrophils, dopamine acts through its receptors to increase formation of extracellular traps and to decrease NO production and transendothelial migration, while having reported bidirectional effects on neutrophil phagocytosis. Dopamine signaling in eosinophils has been shown to affect eosinophil counts with high doses of dopamine leading to eosinopenia and low doses of dopamine leading to eosinophilia. In mast cells, dopamine acting at D1-like receptors has been shown to increase degranulation while D2-like receptor stimulation decreases cytokine production. Created with BioRender.com.