Fig. 4: Synthesis of new fluorinated macrolide antibiotics and 14-membered macrolactones.
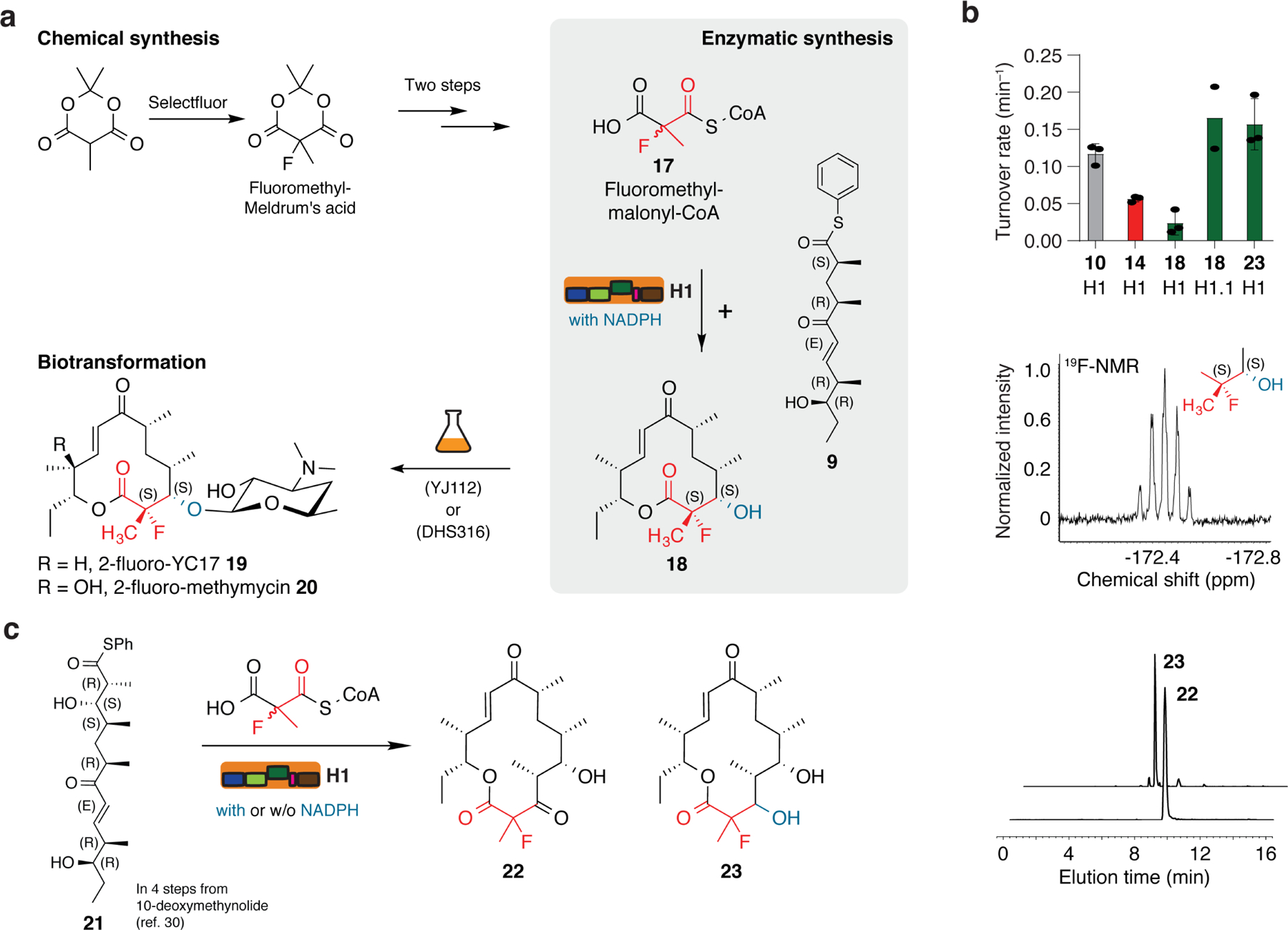
a, Chemoenzymatic approach to establish the MeFC unit at position C-2 in the macrolactone 10. Chemical synthesis was performed analogously to 1 from the respective Meldrum’s acid and the product was converted enzymatically with pentaketide 9 and NADPH to macrolactone 18. Compound 18 was transformed to the fluorinated derivatives of the antibiotic YC-17 (19) and methymycin (20) using the strain DHS316 or YJ112 37. b, Selected data on target compounds and enzymatic turnover. Turnover rates for the H1- and H1.1-mediated conversion of pentaketide 9 and hexaketide 21 with MM-CoA, F-Mal-CoA and F-MM-CoA yielding compounds 10, 14, 18 and 23, respectively. Each data point reflects an independent experiment (biological replicate); mean standard deviations are given, except for H1.1 data (left panel). Elongation using the substrate F-MM-CoA with subsequent reduction to compound 18 can be verified by the multiplicity in 19F-NMR as a quintet (middle panel). The production of compounds 22 and 23 was demonstrated by HPLC-HRMS (EIC: 22 [M+H]+ m/z = 371.2225; 23 [M+H]+ m/z = 373.2384 (right panel). c, Reaction scheme for the H1-mediated conversion of hexaketide 21 with F-MM-CoA to 2-fluoro-narbonolide (22) as well as the reduced analog (23) (for details of the synthesis, see Supplementary Fig. 14).
