Figure 5. pCRP*/mCRP‐driven exacerbation of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury is reduced by C10M.
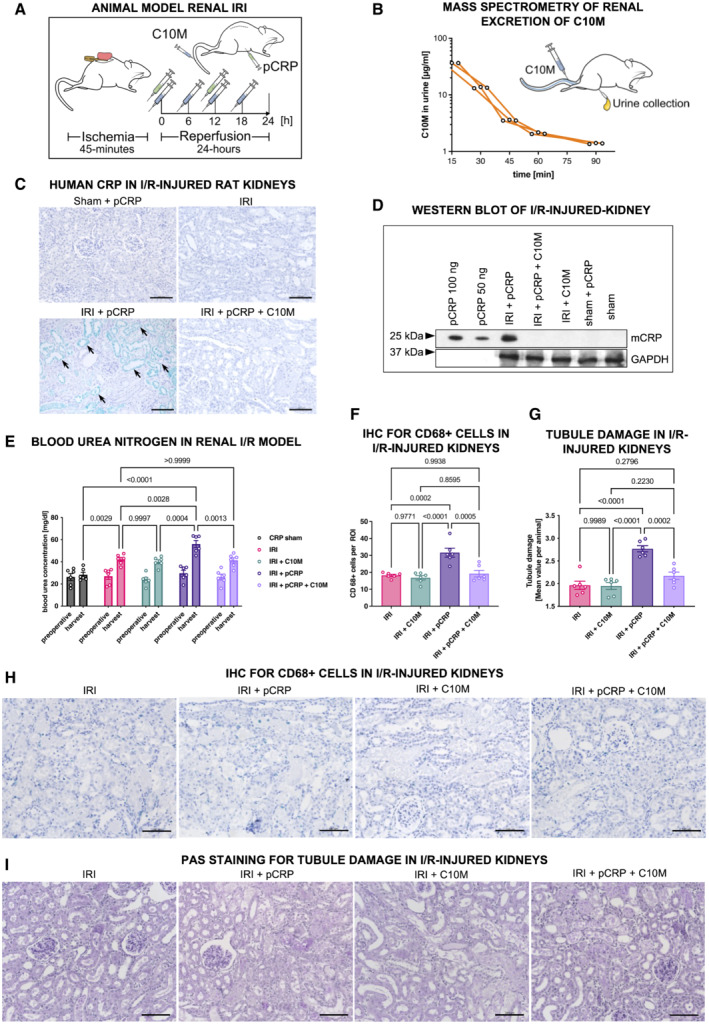
- Depiction of the experimental protocol used for ischemic acute kidney injury. Male Wistar rats were subjected to IRI and received i.p. DPBS and pCRP twice (green syringe). C10M was i.v.‐injected separately every 6 h (blue syringe).
- Detection of C10M by mass spectrometry in rat urine. Renal excretion of C10M detected by mass spectrometry in three rats (biological replicates, n = 3) intravenously injected with C10M. Urine samples were collected at the indicated timepoints. 80% of the applied C10M mass was excreted after 90 min (Kather et al, 2021).
- Immunohistochemistry of rat kidneys subjected to IRI and i.p. pCRP application revealed distinct staining by anti‐pCRP*/mCRP‐9C9 antibody (green, arrows). C10M reduces the deposition of total CRP in the impaired tissue. No deposits in the non‐ischemic tissue (sham). Exemplary stainings out of at least three are shown. Scale bars, 100 μm.
- Tissue lysates of rat kidney were separated on SDS‐PAGE and total CRP was identified with anti‐CRP antibody. A band at the size of mCRP (~ 23 kDa) was detected in kidneys subjected to IRI and pCRP, but not in animals treated additionally with C10M. The household gene protein GAPDH served as a control for loading equal amounts of protein. 50 and 100 ng human pCRP, respectively, served as a positive control. Representative results are shown for replicated assays (n = 3).
- Renal excretion is impaired by pCRP*/mCRP‐driven tissue damage. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) was utilized as surrogate marker for the excretion function of the kidney. Blood samples were taken before the surgical procedure (preoperative) and 24 h after the procedure (harvest). Graph shows mean ± SEM.
- Immunohistochemical detection of transmigrated CD68+ cells in IRI kidneys. Quantification of immunohistochemical results is shown as mean ± SEM. pCRP (25 μg/ml) increased the number of CD68+ cells transmigrated into injured renal tissue significantly, while C10M abolished these effects. Presented are mean cell counts per ROI in each animal.
- Periodic acid‐Schiff (PAS) stained kidney sections show increased damage after renal IRI in rats when pCRP (25 μg/ml) was injected i.v. The tubulointerstitial injury was quantified by the loss of tubular brush border and by cast formation following an established protocol (Megyesi et al, 1998, 2001). Quantification of immunohistochemical results is shown as mean ± SEM.
- Representative results for the immunohistochemical detection of transmigrated CD68+ cells in IRI kidneys. CD68+ cells are stained with HistoGreen substrate (green). Scale bars indicate 100 μm.
- Representative results for the PAS stained kidney sections quantified in (G). Scale bars indicate 100 μm.
Data information: Statistical analysis (E–G) was performed with ANOVA and Tukey's post‐hoc test. Biological replicates, n = 6, precise P‐values are given.
Source data are available online for this figure.
