Fig. 1.
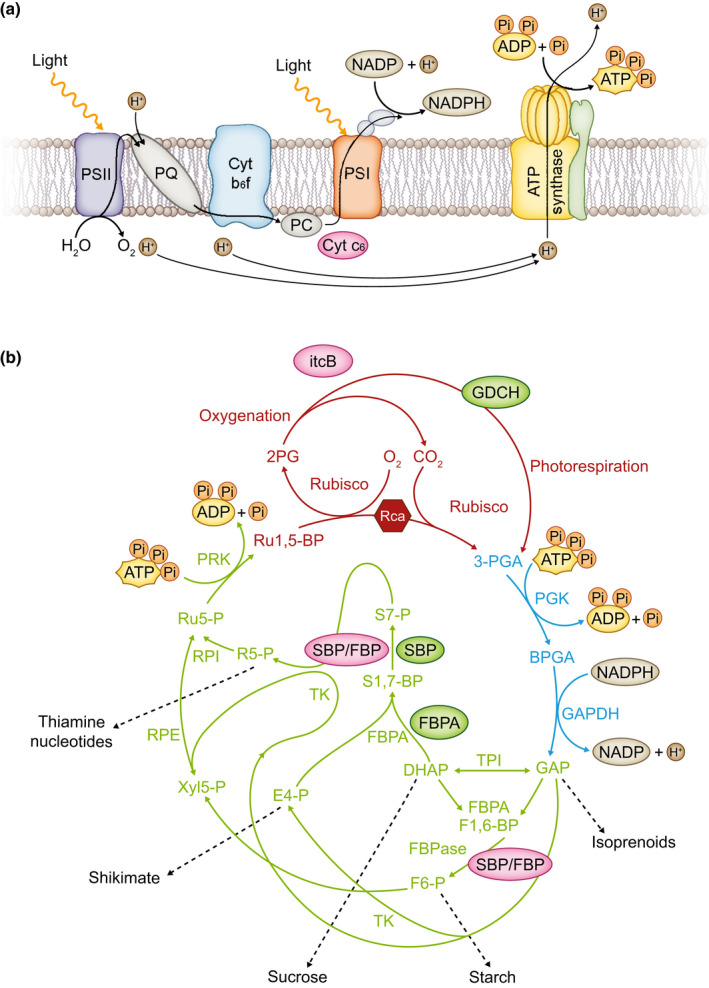
The Calvin–Benson–Bassham (CBB) cycle. (a) Energy in the form of ATP and NADPH needed to drive the CBB cycle is produced in the thylakoid membrane‐located electron transport chain. (b) The first step in the CBB cycle is catalysed by ribulose 1,5‐bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) resulting in the formation of 3‐phosphoglycerate (3‐PGA). The next two reactions form the reductive phase and are catalysed by phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK), forming glycerate 1,3‐bisphosphate (BPGA) using ATP and glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) which forms glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate (GAP) consuming NADPH. Triose phosphate isomerase (TPI) catalyses the production of dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and together with GAP enters the regenerative phase of the cycle, catalysed by fructose 1,6‐bisphosphate/sedoheptulose 1,7‐bisphosphate aldolase (FBPA), forming sedoheptulose 1,7‐bisphosphate (S1,7‐BP) and fructose 1,6‐bisphosphate (F1,6‐BP). Sedoheptulose 1,7‐bisphosphatase (SBPase) and FBPase (fructose 1,6‐bisphosphatase) then produce sedoheptulose 7‐phosphate (S7‐P) and fructose 6‐phosphate (F6‐P), which are converted to 5C compounds in reactions catalysed by transketolase (TK), ribose 5‐P isomerase (RPI) and ribulose 5‐phosphate epimerase (RPE), resulting in the formation of ribulose 5‐P (Ru5P). The final step in the cycle is catalysed by ribulose 5‐phosphate kinase (PRK), producing the CO2 acceptor molecule ribulose 1,5‐bisphosphate (Ru1,5‐BP). The three phases of the CBB cycle are shown: (1) carboxylation (red), (2) reduction (blue) and (3) regeneration (green). The products of the CBB cycle are exported to a number of biosynthetic pathways (grey dashed lines): isoprenoid, starch, sucrose, shikimate, thiamine and nucleotide. Rubisco has a competing oxygenase reaction which results in the formation of 2‐phosphoglycerate, which enters the photorespiratory pathway. The manipulations related to ribulose‐1‐5 bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration discussed in this paper are in the electron transport chain algal cytochrome C6 (CytC6), the photorespiratory cycle H‐subunit of glycine decarboxylate (GDCH), the putative transporter from an alga (ictB), the endogenous SBPase and FBPA enzymes and the cyanobacterial bifunctional sedoheptulose 1,7‐bisphosphatase/fructose 1,6‐bisphosphatase (SBPase/FBPase) enzyme. Overexpression of endogenous proteins is shown in green and foreign proteins in pink.
