Fig. 1.
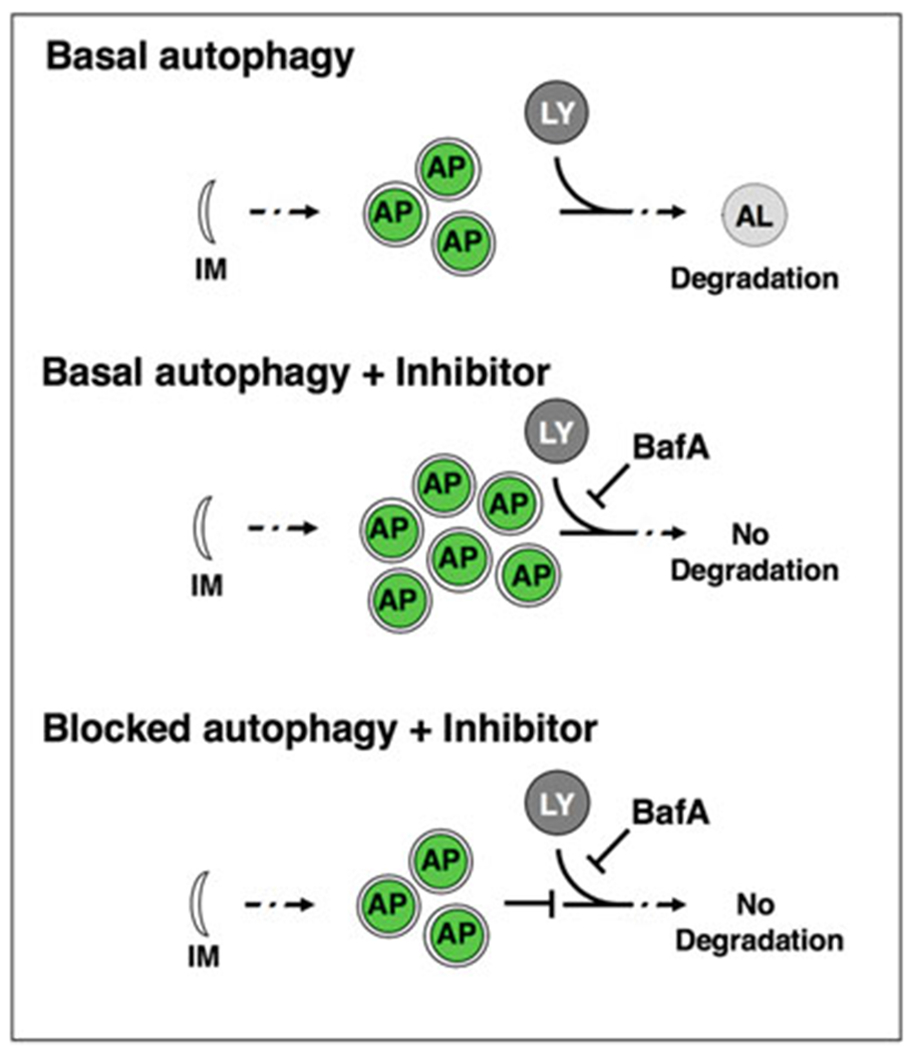
Autophagy flux assay. Basal autophagy is initiated with the nucleation of a double membrane (isolation membrane, IM), which forms the phagofore. The phagofore expands into an autophagosome (AP) that sequesters cytosolic material (also referred to as cargo) destined for degradation. Autophagosomes fuse with acidic lysosomes (LY) to form autolysosomes (AL), in which the cargo is subsequently degraded. In autophagy flux assays, the chemical autophagy inhibitor Bafilomycin A (BafA) can be used to block autophagic turnover. In situations where autophagy is active, the addition of BafA will change the apparent number of autophagosomes. If autophagy is blocked, BafA addition will not change the number of autophagosomes compared to control conditions
