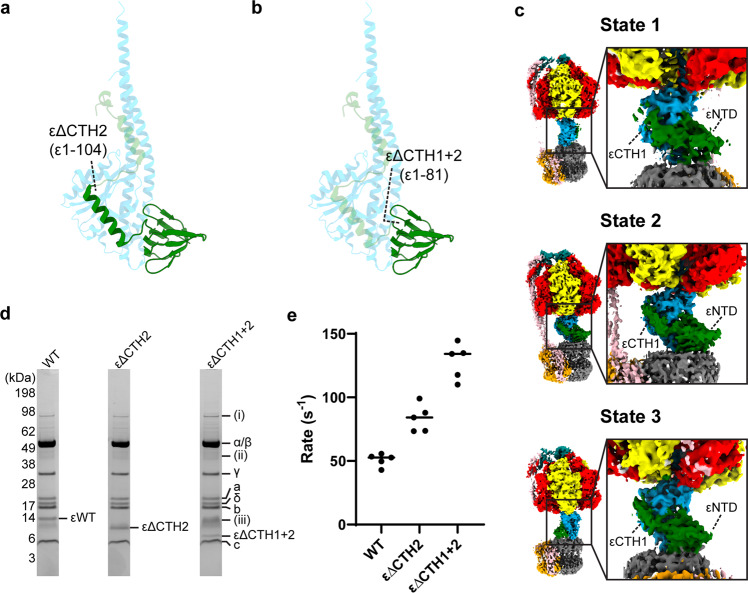
Fig. 7. Subunit ε attenuates ATPase activity.
a εΔCTH2 truncation retains the εCTH1 which can bind to the γ subunit. b εΔCTH1 + 2 retains only the εNTD akin to the εCTD down conformation. c Cryo-EM maps of the 3 states generated using the εΔCTH2 truncation mutant after exposure to 10 mM MgATP showed E. coli F1Fo ATP synthase in the half-up sub-state, with εCTH1 attached to the subunit γ. The 3 states have been rotated successively by 120° to show the position of subunit ε. d Coomassie stained SDS PAGE (uncropped image provided as Supplementary Data 5) of purified E. coli F1Fo ATP synthase WT, εΔCTH2 and εΔCTH1 + 2. Subunits labeled and minor contamination bands identified as; (i) Ribonuclease E, (ii) GroEL, and (iii) ElaB. e ATP regeneration assays of WT (containing full length subunit ε), εΔCTH2 (ε1–104) and εΔCTH1 + 2 (ε1–81). All data points and mean are shown (raw traces are in Supplementary Fig. 8 and values in Supplementary Data 6). Removal of εCTH2 results in higher ATP turnover than WT. Removal of both εCTH1 and εCTH2 shows higher ATP turnover than removal of only εCTH2.