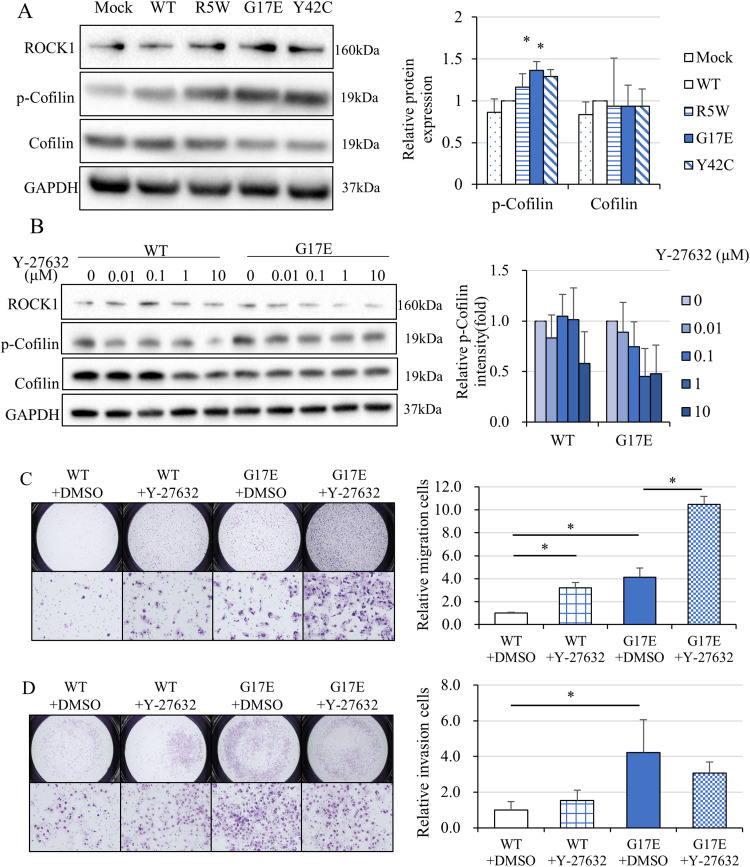
Figure 3.
Introduction of RhoA mutations activated the ROCK signaling pathway, whereas inhibition of the ROCK signaling pathway unexpectedly enhanced cell motility. (A) Protein expression of the RhoA-ROCK signaling pathway in MKN74 cells transduced with a vector containing RhoA mutants. Transduction of the RhoA G17E and Y42C mutant-containing vector enhanced the expression of ROCK and phosphorylated cofilin proteins (N = 4). (B) The ROCK inhibitor, Y-27632, suppressed the RhoA G17E-induced phosphorylation of cofilin in a concentration-dependent manner (N = 4). (C) Migration and invasion assays of MKN74 cells transduced with RhoA WT and the RhoA G17E mutant using a transwell system with 10 μM Y-27632 (N = 4). Inhibition of the ROCK signaling pathway unexpectedly enhanced cell motility in both RhoA WT- and RhoA G17E-containing cells. (D) Invasion assays of MKN74 cells transduced with a RhoA WT- or RhoA G17E mutant-containing vector using a Matrigel-coated transwell system with 10 μM Y-27632 (N = 4). Cell invasion was promoted significantly in cells with RhoA WT but was not significantly changed in cells with the RhoA G17E mutant (N = 4). *P < 0.05.