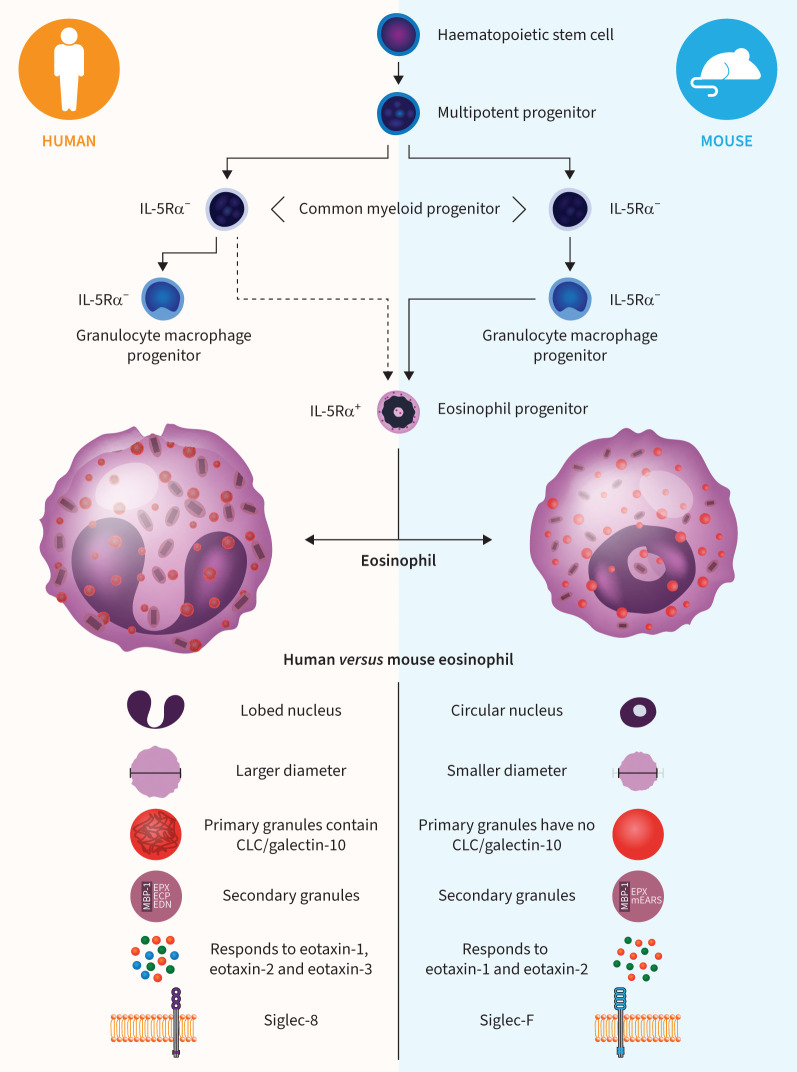
FIGURE 1.
Development and characteristics of human and mouse eosinophils [1–3]. Several differences have been noted between mature eosinophils from humans versus mice. Human eosinophils are larger than mouse eosinophils, stain more intensely with eosin and have a lobed rather than a circular nucleus. Primary granules in human (but not mouse) eosinophils contain Charcot–Leyden crystal (CLC) protein/galectin-10. The dense core of secondary granules in both human and mouse eosinophils is predominantly composed of major basic protein-1 (MBP-1). Eosinophil-associated RNases in human secondary granules include eosinophil protein X (EPX), eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN). Eosinophil peroxidase is stored in secondary granules in both human and mouse eosinophils. Human eosinophils respond to eotaxin-1 (CCL11), -2 (CCL24) and -3 (CCL26), whereas mouse eosinophils respond to eotaxin-1 and -2. Among cell surface molecule differences, human eosinophils express Siglec-8 and mouse eosinophils express Siglec-F. CCL: chemokine (CC motif) ligand; IL-5Rα: interleukin-5 receptor α; mEARS: mouse eosinophil associated RNases. Development schematic adapted from Lee et al. [1] with permssion.