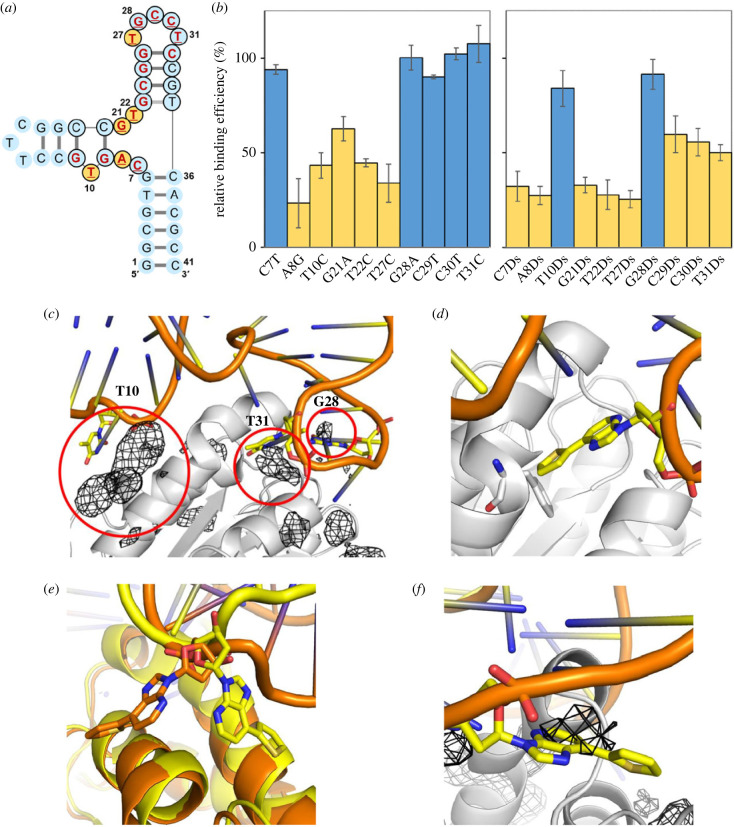
Figure 3.
Binding of ARC1172 variants with vWF. (a) Schematic illustration of ARC1172. Nucleotides with bold red letters are within 4.2 Å of vWF in the complex [34]. The consensus nucleotides identified for high-affinity binding to vWF are indicated in black circles [34]. The 10 positions for point mutations (transition or Ds incorporation) are underlined. The essential bases assigned from the EMSA (electronic supplementary material, figure S8) are shown in orange circles. (b) Relative binding efficiencies (%) of ARC1172 variants with vWF. The positions that exhibited less than 65% of the relative binding efficiencies (average) were assigned as the essential base positions and are shown by orange bars. (c) Binding sites detected near the aptamer–vWF binding interface. Benzene occupancy maps (black mesh) overlaid on the structure of ARC1172 complexed with vWF (PDB 3HXQ), with detected binding sites near the aptamer–vWF binding interface circled in red. vWF is shown in white, and the aptamer is shown in yellow and orange. (d) Modelled structure of the vWF–ARC1172 (T31Ds) complex, showing steric clash between Ds31 (yellow) and Phe1397 (white). (e) MD snapshots of the vWF–ARC1172 (T10Ds) complex, showing alternative conformations of Ds10 (yellow and orange). (f) MD snapshot of the vWF–ARC1172 (G28Ds) complex, showing the overlap of Ds28 with the benzene map densities (black mesh). (Online version in colour.)