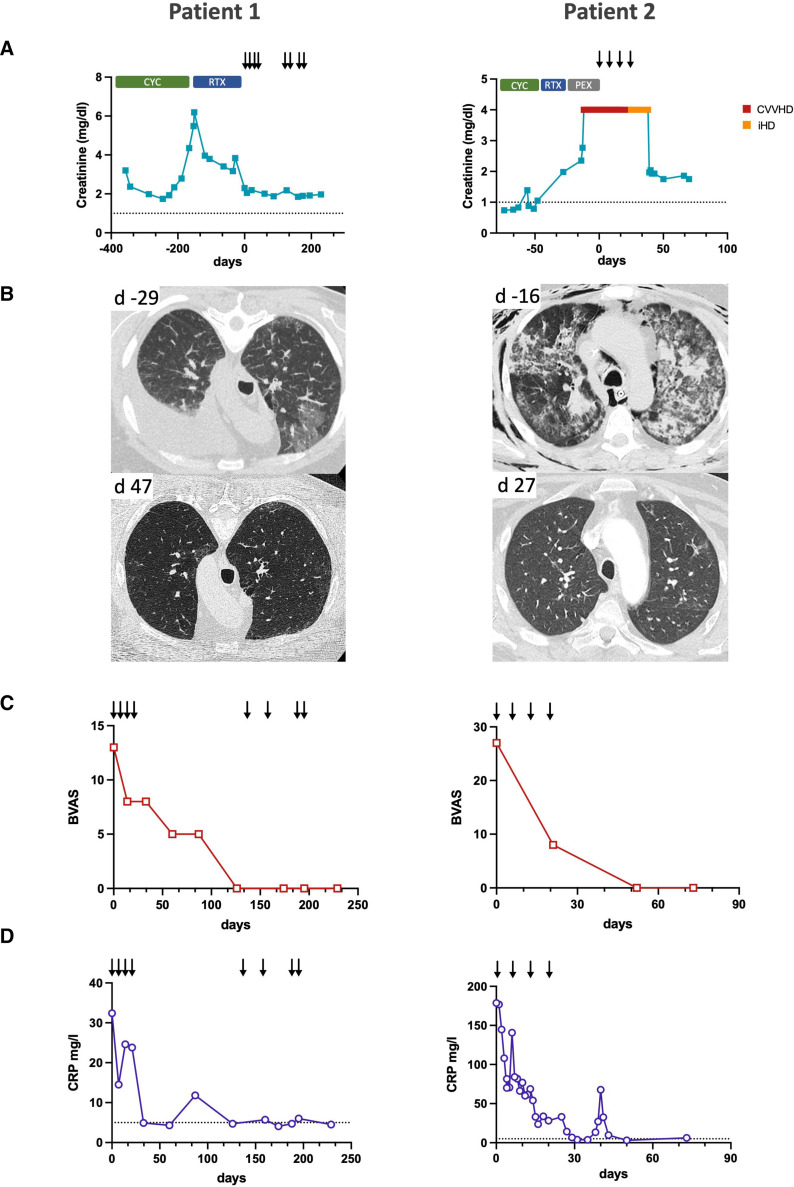
Figure 1.
Improvement of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis (AAV) disease activity after daratumumab treatment. (A) Serum creatinine levels before and after daratumumab treatment. Previous induction therapies with cyclophosphamide (CYC), rituximab (RTX) and plasma exchange (PEX) did not lead to clinical remission or stabilisation of kidney function. Arrows indicate daratumumab doses, the dotted line indicates the upper normal limit for serum creatinine. Patient 2 underwent renal replacement therapy with continuous veno-venous haemodialysis (CVVHD) and intermittent haemodialysis (iHD). (B) CT of lung sections showing pleural effusion and alveolitis (patient 1) and AAV-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome and ventilator-associated soft tissue emphysema (patient 2). Only some fibrotic changes remain after daratumumab treatment. (C) Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS) shows clinical remission after daratumumab treatment. (D) C reactive protein (CRP) levels in both patients decline to normal levels after daratumumab treatment, the dotted line indicates the upper normal limit.