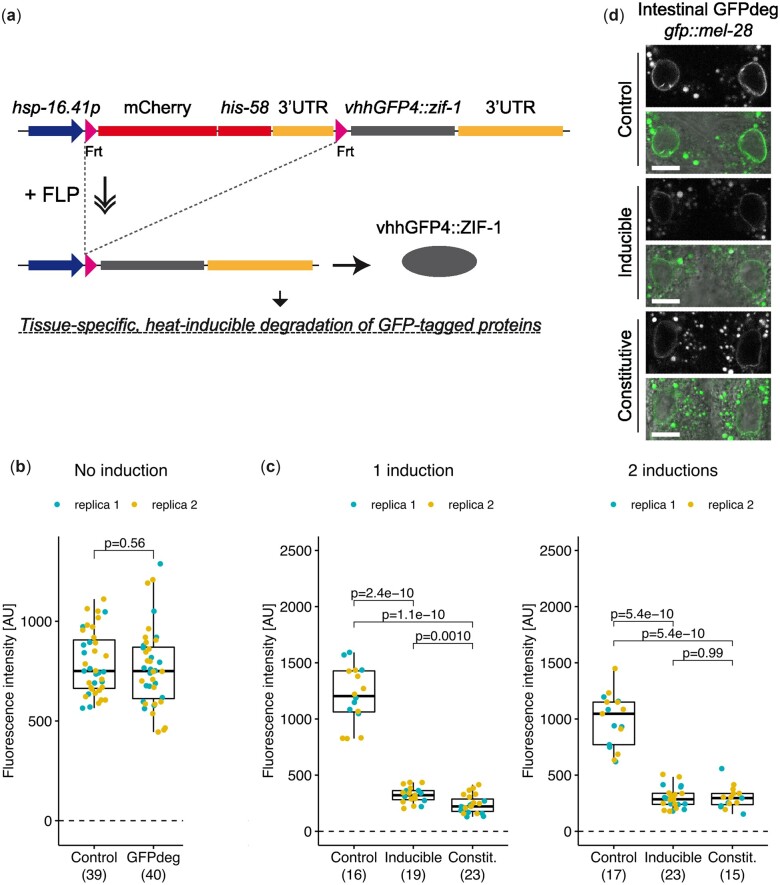
Fig. 4.
Degradation of GFP::MEL-28 in intestinal cells. a) Schematic representation of the GFPdeg strategy. The vhhGFP4::ZIF-1 fusion protein targets GFP-tagged proteins for rapid degradation. Temporal and spatial control is provided by the hsp-16.41 promoter and tissue-specific FLP expression, respectively. b) Quantification of GFP::MEL-28 at the nuclear envelope of hypodermal nuclei of young adults either without the GFPdeg system (Control; strain BN452) or with the GFPdeg system but without induction (GFPdeg; strain BN1084). P-value from t test is indicated. c) Quantification of GFP::MEL-28 at the nuclear envelope of anterior intestinal nuclei of young adults after 1 or 2 rounds of GFPdeg induction in the intestine (elt-2p::FLP driver; strain BN1118). Control (strain BN452) and constitutive degradation (elt-2p::vhhGFP4::zif-1; strain BN746) are included for comparison. Graph details are explained in Fig. 3. P-values from pair-wise t tests and adjusted for multiple comparisons (Benjamini and Hochberg method) are indicated. d) Confocal micrographs of gfp::mel-28 young adults without GFPdeg (top panels; strain BN452), inducible intestinal GFPdeg (middle panels; strain BN1118) or constitutive intestinal GFPdeg (bottom panels; strain BN746). A single focal plane of the anterior pair of intestinal nuclei is shown. Scale bar 10 µm.