Fig. 3.
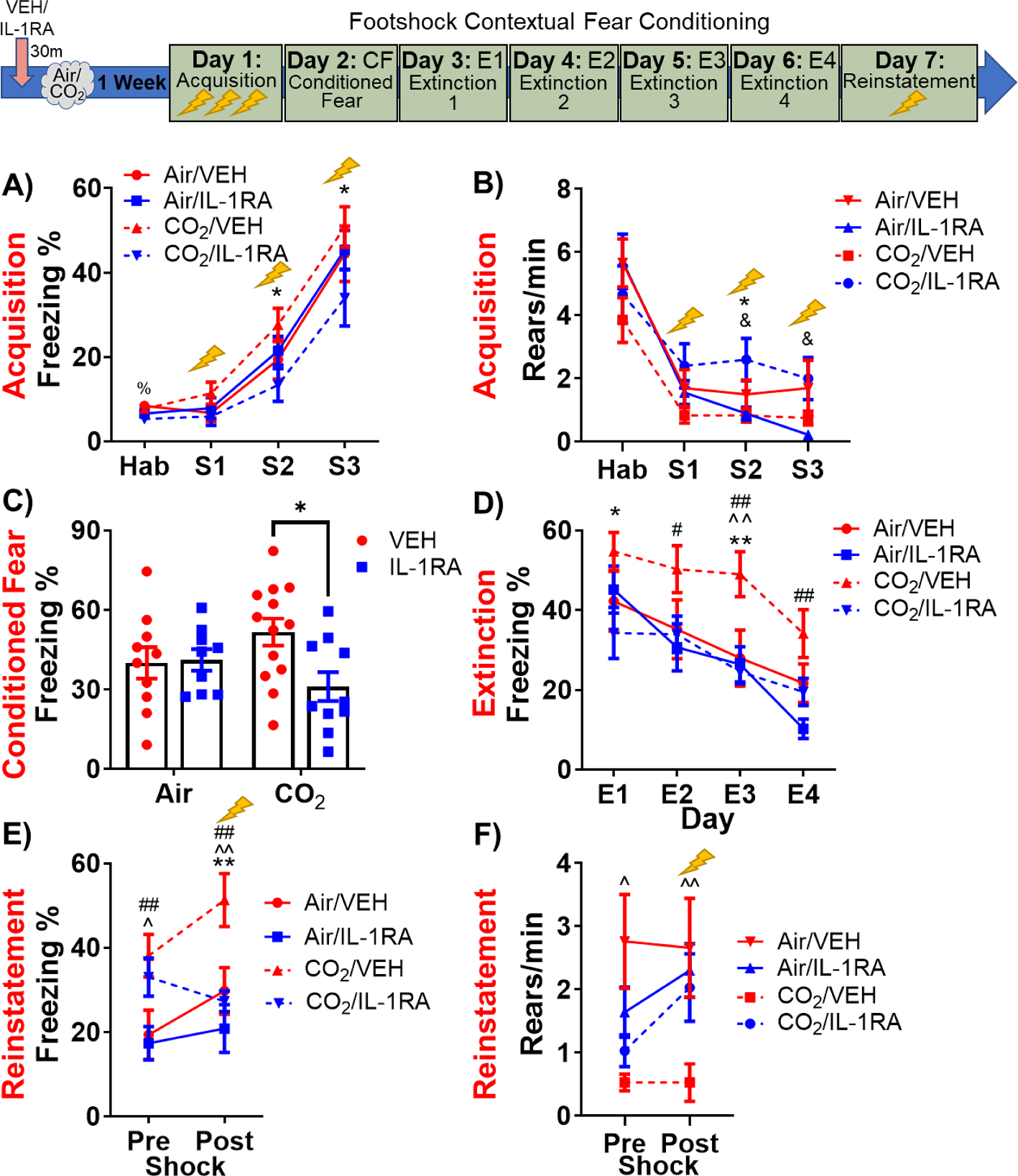
SFO-IL-1R1 signaling modulates delated effects of CO2 on active and passive behaviors during contextual fear conditioning, extinction and reinstatement. Top panel shows the layout of the fear conditioning paradigm. See Fig. 1 for full experimental layout (mice received SFO-targeted infusions of IL-1RA or vehicle 30 min prior to CO2 or air exposure a week prior to fear conditioning). A) On fear acquisition day, SFO-IL-1RA infusion one week earlier significantly reduced freezing following foot shocks only in mice previously exposed to CO2 inhalation. No significant treatment effects were observed in air-exposed mice. B) In response to foot shock, prior IL-1RA treatment increased rearing in previously CO2– exposed mice, but not air- exposed mice. C) Prior IL-1RA treatment attenuated conditioned freezing 24 h post-shock in previously CO2– exposed mice, but not air- exposed mice. D) Prior IL-1RA treatment also attenuated the heightened freezing during extinction in CO2-exposed mice, with no effects in air- exposed mice. Additionally, prior IL-1RA treatment attenuated freezing responses (E) and increased rearing responses (F) to a reminder foot shock during fear reinstatement only in mice previously exposed to CO2 inhalation. Data are mean ± SEM. CO2/VEH vs CO2/IL-1RA: *p < 0.05 **p < 0.01; CO2/VEH vs Air/VEH: ^p < 0.05 ^^p < 0.01; CO2/VEH vs Air/IL-1RA: #p < 0.05 ##p < 0.01; Air/IL-1RA vs CO2/IL-1RA: &p < 0.05; Air/VEH vs CO2/IL-1RA: %p < 0.05. (n = 9–13) H = Habituation, S = Shock 1, 2, or 3, E = Extinction Day.
