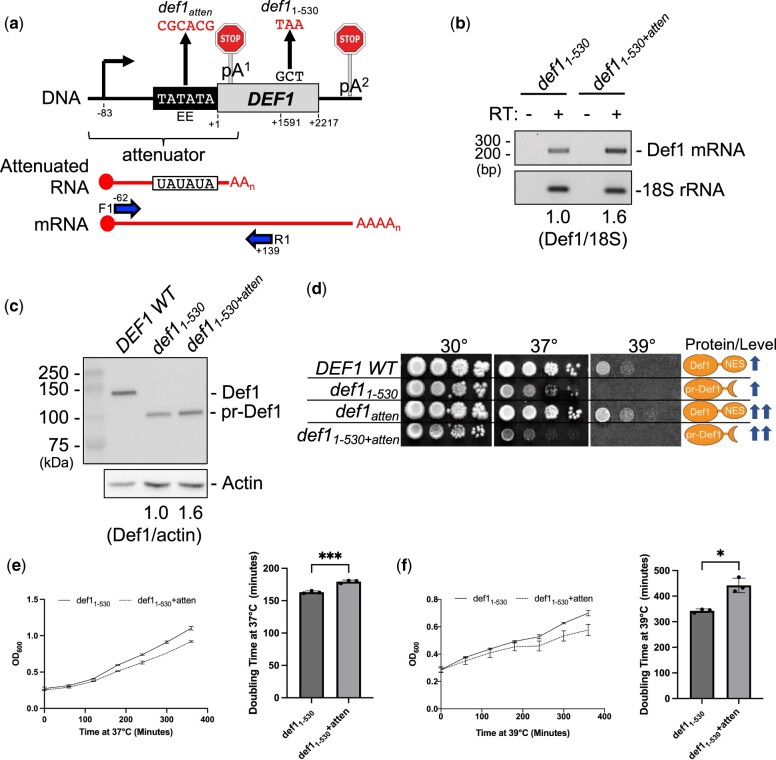
Fig. 2.
The def1 attenuator mutant (def1atten) overexpresses mRNA and protein, exacerbating the cell toxicity of processed Def1 (def11–530). a) Schematic of def1 mutants (def1-atten and def11–530) along with RT-PCR primers (F1, R1, blue) used to detect the DEF1 mRNA readthrough product. Note: the drawing is not to scale. The R1 primer is specific to longer mRNA and not attenuated RNA. DNA positions are numbered relative to the +1 start codon of the DEF1 open reading frame. b) RT-PCR analysis of Def1 mRNA levels. 18S serves as a loading control for total RNA. Reverse Transcriptase (±RT) ensures that signal is dependent on RNA and not genomic DNA template. c) Western blot analysis of Def1 protein levels. Actin serves as a loading control for total protein. d) Spot test assay of def1 mutants on solid plate media. Liquid cultures were grown to saturation at 25°C, serially diluted, spotted onto YPAD, and grown at the temperatures indicated for 3–5 days. e, f) Growth of def1 mutants in liquid culture. Liquid yeast cultures were grown to saturation at 25°C, diluted back, and recovered to exponential phase prior to shifting to (e) 37°C or (f) 39°C for 6 h. Cell density was measured via OD600 every hour, and doubling times were calculated from exponential lines of best fit for data between 60 and 360 min. Error bars represent SD from 3 biological replicates. Asterisks indicate statistical significance by Welch’s 2 sample t-test (*P ≤0.05, **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001, ****P≤0.0001, ns—not significant).