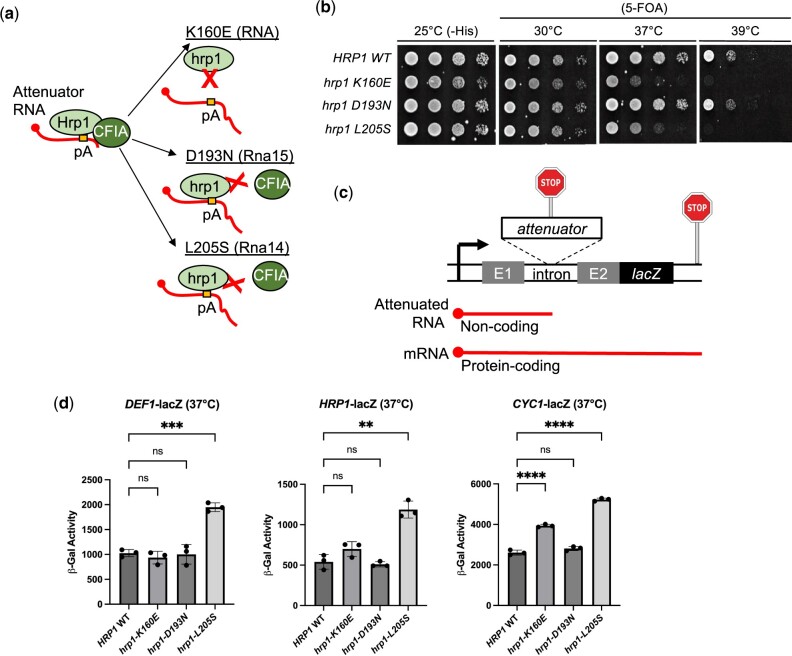
Fig. 4.
Hrp1 function in attenuator recognition is dependent on its interaction with CFIA and RNA and varies based on the Pol II terminator. a) Schematic of Hrp1 activity and hrp1 mutants expected to disrupt interaction with RNA (K160E), CFIA protein Rna15 (D193N), or CFIA protein Rna14 (L205S). b) Spot test growth assay of hrp1 mutants. A yeast shuffle strain [hrp1::KANMX, pRS316-HRP1 (URA3)] was transformed with HIS3-marked plasmids containing hrp1 mutants prior to 5-FOA shuffling. Serial dilutions were spotted on plates and grown 3 days at indicated temperatures. c) Schematic of attenuator-lacZ reporter gene system. d) Attenuator functionality assays using a lacZ reporter gene with hrp1 mutants. Yeast strains bearing HRP1 WT or hrp1 mutant plasmids were transformed with lacZ reporter genes containing DEF1 or HRP1 attenuators. The CYC1 terminator serves as a control for hybrid termination. Overnight cultures were grown to saturation at 30°C and recovered to exponential phase followed by a 2-h shift to nonpermissive temperature (37°C). Cells were lysed and β-galactosidase activity was measured to detect attenuator readthrough. Error bars represent SD of 3 biological replicates. Asterisks indicate statistical significance by Welch’s ANOVA.