Fig. 5.
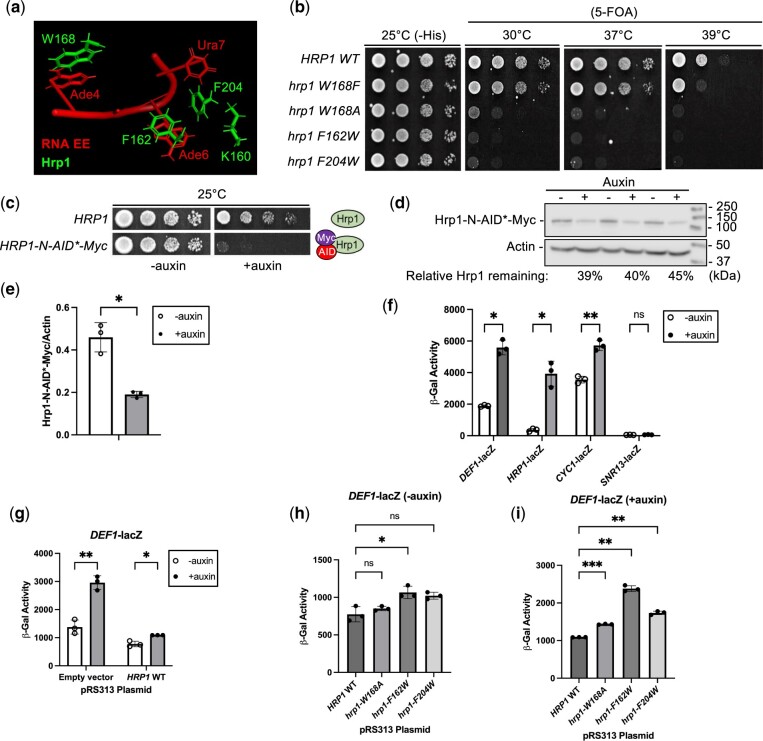
The hrp1 RRM1 mutants W168A, F162W, and F204W are lethal and defective for attenuation. a) Protein–RNA interface for the Hrp1-EE complex (structure 2KM8; PyMOL). Relevant Hrp1 side chains (green) and RNA bases (red) are represented in stick format. b) Spot test growth assay of hrp1 mutants. A yeast shuffle strain [hrp1::KANMX, pRS316-HRP1 (URA3)] was transformed with plasmids containing hrp1 mutants prior to 5-FOA shuffling. Serial dilutions were spotted on plates and grown 3 days at indicated temperatures. c) Yeast strains containing osTIR1 and WT (HRP1) or an N-terminal degron tag (HRP1-N-AID*-Myc) were grown on YPAD ± auxin inducer (1 mM) for 3 days. d) Western blot analysis of Hrp1 depletion. Hrp1 degron strains (in biological triplicate) were grown in YPAD until exponential phase, followed by treatment with auxin (1 mM) or ethanol solvent control for 4 h. Hrp1 was detected from protein extracts with an anti-Myc antibody and normalized to actin as a loading control. e) Average Hrp1 protein levels were quantified from 3 biological replicates, and error bars represent SD. f) The Hrp1 degron strain (HRP1-N-AID*-Myc) was transformed with lacZ reporter genes and grown in selective media ± auxin for 4 h. Cells were lysed and β-galactosidase activity was measured to detect attenuator readthrough. Error bars represent SD of 3 biological replicates. g–i) The Hrp1 degron strain containing DEF1-lacZ was transformed with pRS313 plasmids containing empty vector, HRP1 WT, or hrp1 mutants. Auxin treatment and β-gal assays were performed as in (f). Asterisks indicate statistical significance by Welch’s 2 sample t-test.