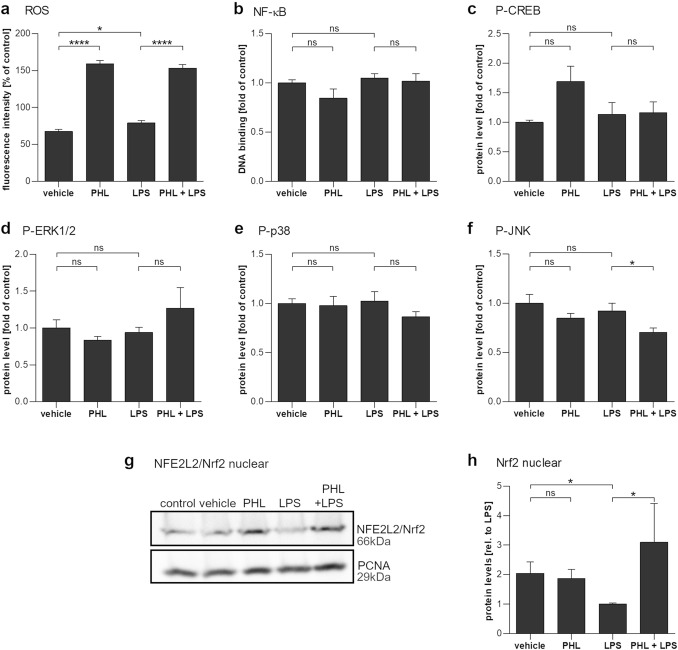
Fig. 5.
The effect of phloretin and LPS exposure on cellular signaling pathways in ARPE-19 cells. a Intracellular ROS levels are significantly increased in cells exposed to 100 µM phloretin (PHL) for 1 h and slightly increased in cells exposed to 10 µg/ml LPS (LPS) for 5 min. b–f Following a 1 h pretreatment with PHL and a 2 h exposure to LPS, the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB subunit p65 (b) or the intracellular levels of phosphorylated CREB (c), ERK1/2 (d), and p38 (e) remained unaffected. The phosphorylation of JNK (f) was reduced by cotreatment with 100 µM phloretin and 10 µg/ml LPS. g/h Phloretin increased the nuclear levels of Nrf2 as determined by Western Blotting (g, quantified h). Data are combined from three or four independent experiments, with two to four parallel samples per experiment and are represented as mean ± SEM. ns not statistically significant, *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001, Mann–Whitney U-test