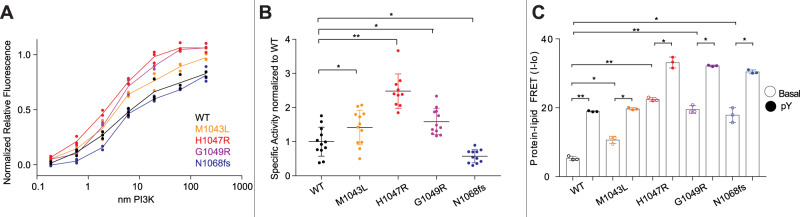
Fig. 4. Biochemical analysis of C-terminal PIK3CA mutations and their effect on membrane binding and ATPase assays.
A Measurement of ATP turnover performed with different p110α constructs in solution. Experiments were performed with 200 to 0.186 nM PI3K, with 100 µM ATP in the absence of lipid vesicles. B Specific activity values normalised to WT for the ATPase assay performed with different p110α constructs in solution (technical replicates, data is presented as mean values, error bars are S.D., n = 10 (H1047R) n = 11 (N1068fs) or n = 12 (WT, M1043L, G1049R.). Experiments were performed with 19.5 to 0.59 nM PI3K, and 100 µM ATP in the absence of lipid vesicles. Two-tailed t-test p-values represented by the symbols are as follows: **<0.001; *<0.05; n.s. > 0.05. C Protein-Lipid FRET assay performed with different p110α and p85α constructs under basal and pY activated states on PM mimic liposomes containing 5% PIP2, 10% Dansyl PS, 15 % PS, 40% PE, 10% cholesterol, 15% PC and 5% SM. Experiments were carried out at saturating concentrations of PI3K (0.5–1 µM) and 16.65 µg/ml of lipid vesicles (mean is shown, with error bars representing S.D., n = 3). Two-tailed t-test p-values represented by the symbols are as follows: **<0.001; *<0.05; n.s. > 0.05. Source data for this figure are provided in the Source Data file.