Figure 5: Metabolic changes downstream of the neurotransmitters glutamate/GABA.
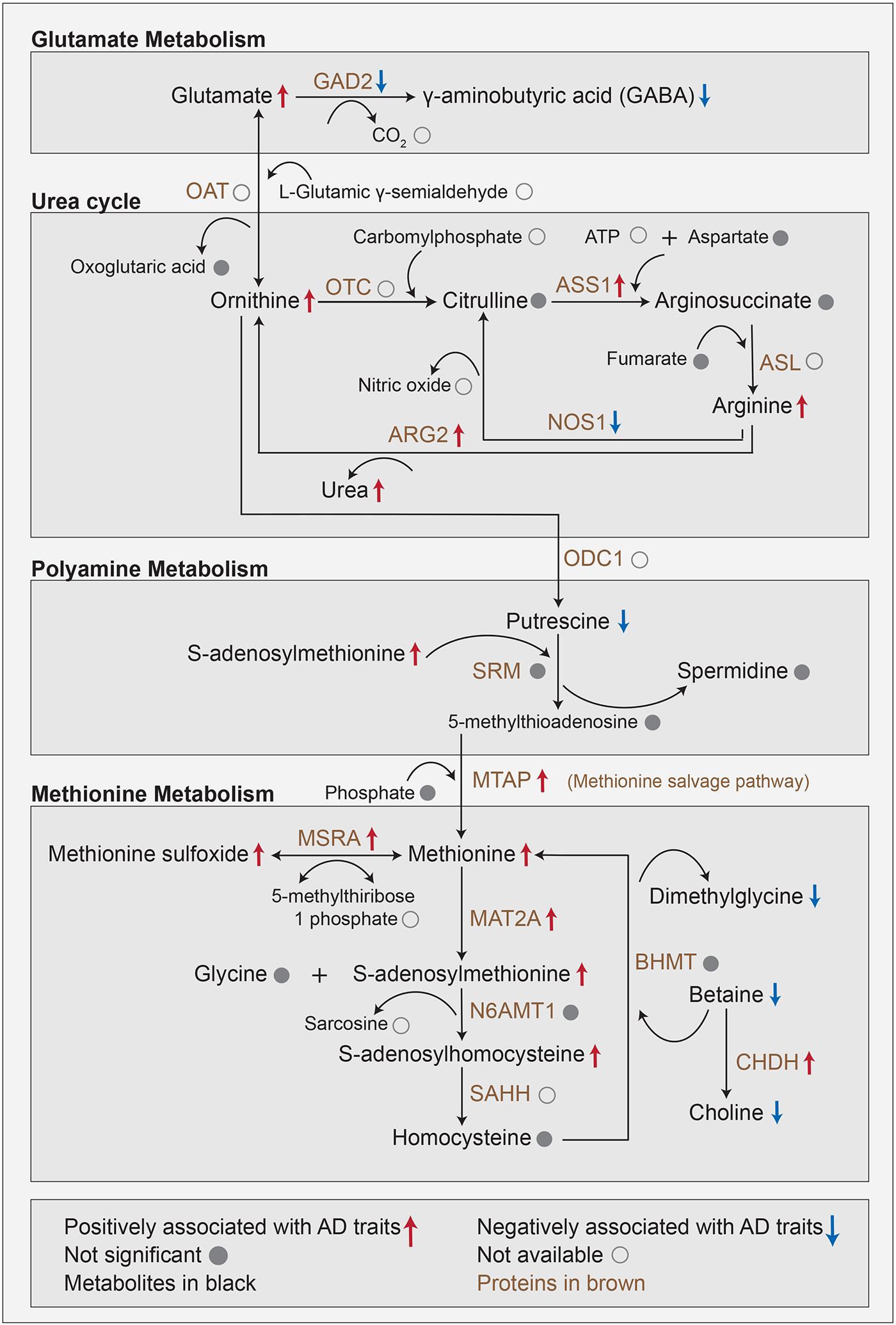
This multi-omics cascade starts with a biochemical process involving the conversion of glutamate into GABA within glutamate metabolism. Glutamate metabolism feeds into the urea cycle by conversion of glutamate to ornithine. Urea buildup to neurotoxic levels has been observed in postmortem brains of Huntington’s disease and has furthermore been linked to dementia. The urea cycle connects to polyamine metabolism via the conversion of ornithine into putrescine. Putrescine promotes the clearance of apoptotic cells via efferocytosis, a mechanism affected in AD. Polyamine metabolism connects to methionine metabolism through the methionine salvage pathway. Methionine acts as an antioxidant and is a precursor of s-adenosylmethionine, which is a key methyl donor in brain cells and involved in the synthesis of the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin via the folate cycle.
