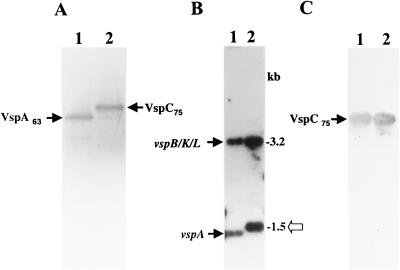
FIG. 1.
(A) Western blot analysis of two M. bovis clonal isolates expressing the VspA (lane 1, clone 7) and VspC (lane 2, clone 168) products. Whole organisms were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with MAb 1E5 (2). The VspA63 and VspC75 products are indicated. (B) Identification of the M. bovis vspC gene. Four-microgram aliquots of chromosomal DNAs of the isolates were digested with HindIII, subjected to Southern blot hybridization, and probed with the γ-32P-labeled ra-4 oligonucleotide. HindIII genomic fragments carrying the vspB, vspK, and vspL genes or the vspA gene are indicated by labeled arrows (14). Molecular size markers are shown on the right. An open arrow marks a 1.5-kb HindIII genomic fragment present in the VspC variant. (C) Expression in E. coli of the recombinant vspC gene. E. coli cells expressing under selective induction of the T7 promoter control the recombinant plasmid pKC75 carrying the vspC gene were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with MAb 1E5 (lane 1). Total mycoplasma proteins of the M. bovis VspC clonal isolate (A, lane 2) were used as a positive control (lane 2). The recombinant VspC product expressed in E. coli as well as the authentic VspC product expressed in the mycoplasma are indicated by arrows.